Expression and clinical significance of mammalian target of rapamycin/P70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in human colorectal carcinoma tissue
- PMID: 26171014
- PMCID: PMC4487095
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3228
Expression and clinical significance of mammalian target of rapamycin/P70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in human colorectal carcinoma tissue
Abstract
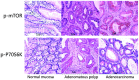
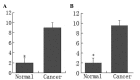
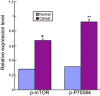
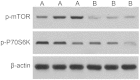
The activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) has been reported in tumor development, but the role of mTOR in colorectal carcinomas remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the significance of mTOR and its downstream effector 70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase (P70S6K) in human colorectal carcinomas. The phosphorylated (p-)mTOR and p-P70S6K proteins were examined by immunohistochemistry performed on tissue microarray containing tissue samples obtained from colorectal carcinoma (n=111), adenomatous polyps (n=40) and normal colonic mucosa (n=40), with a comparison between the expression of these proteins and the clinicopathological parameters of patients with carcinomas. The positive expression rates of p-mTOR and p-P70S6k were 60.4 and 65.8%, respectively, in colorectal carcinoma tissue, which was significantly increased compared with the tissue from adenomatous polyps (27.5 and 20%, respectively) and normal colonic mucosa (10.0 and 5.0%, respectively) (P<0.05). Overexpression of the p-mTOR and p-P70S6K proteins was significantly associated with the tumor-node-metastasis stage, the occurrence of distal and lymph node metastasis and the degree of differentiation. Aberrant expression of p-mTOR and p-P70S6K may contribute to the pathogenesis, growth, invasion and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. The phosphorylation of these proteins was considered to be a promising marker to indicate the aggressive behaviors and prognosis of colorectal carcinomas. The overexpression of the mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathway may play an important role in colorectal carcinoma carcinogenesis. The expression of p-mTOR and p-P70S6K was considered as a promising marker to indicate the aggressive behaviors and prognosis of human colorectal carcinomas.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; immunohistochemistry; mammalian target of rapamycin/70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase; reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of gastric carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study on tissue microarray.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Dec 13;28(1):152. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-152. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 20003385 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of mTOR and p-mTOR protein expression in human colorectal carcinomas.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(10):2581-4. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 22320958
-
Phosphorylated p70S6K expression is an independent prognosticator for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Surgery. 2015 Mar;157(3):570-80. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.10.014. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Surgery. 2015. PMID: 25726316
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of the mammalian target of rapamycin signalling pathway in extramammary Paget's disease.Br J Dermatol. 2009 Aug;161(2):357-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09179.x. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Br J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19438435
-
Morphoproteomics demonstrates activation of mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in papillary thyroid carcinomas with nuclear translocation of MTOR in aggressive histological variants.Mod Pathol. 2011 Dec;24(12):1553-9. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.121. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Mod Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21822208
Cited by
-
Aberrant overexpression of ADAR1 promotes gastric cancer progression by activating mTOR/p70S6K signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):86161-86173. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13354. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27863387 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of mTOR and p-mTOR expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 23;101(51):e32340. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032340. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36595789 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of mTOR and phosphorylated mTOR expression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 11;16(1):877. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2940-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27835987 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of eukaryotic protein kinases by Pin1, a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase.Adv Biol Regul. 2023 Jan;87:100938. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2022.100938. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Adv Biol Regul. 2023. PMID: 36496344 Free PMC article.
-
S6K1 blockade overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncogene. 2020 Dec;39(49):7181-7195. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01497-4. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 33037411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, corp-author. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
