Radiosensitization of human glioma cells by tamoxifen is associated with the inhibition of PKC-ι activity in vitro
- PMID: 26171054
- PMCID: PMC4487191
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3195
Radiosensitization of human glioma cells by tamoxifen is associated with the inhibition of PKC-ι activity in vitro
Abstract
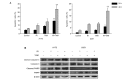
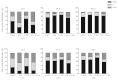
The present study aimed to investigate the radiosensitizing effects of tamoxifen (TAM), a non-steroidal anti-estrogen drug, in human glioma A172 and U251 cells in vitro. A colony-forming assay revealed that TAM enhances radiosensitivity in A172 and U251 cells. Treatment with TAM also increased the percentage of apoptotic cells subsequent to ionizing radiation, and increased the expression of apoptotic markers, including cleaved caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Ionizing radiation induced G2/M phase arrest, which was alleviated within 24 h when the radiation-induced DNA damage was repaired. However, flow cytometry analysis revealed that TAM treatment delayed the recovery of cell cycle progression. Additional examination demonstrated that TAM-mediated protein kinase C-ι (PKC-ι) inhibition may lead to the activation of pro-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2-associated death promoter, and the dephosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, resulting in increased cell apoptosis and sustained G2/M phase arrest following exposure to radiation. The present data indicate that the radiosensitizing effects of TAM on glioma cells are partly due to the inhibition of PKC-ι activity in vitro.
Keywords: Bad; cyclin-dependent kinase 7; glioma; protein kinase C-ι; radiosensitivity; tamoxifen.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Measuring the lactate-to-creatine ratio via 1H NMR spectroscopy can be used to noninvasively evaluate apoptosis in glioma cells after X-ray irradiation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Jun 15;23:27. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0092-2. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29946338 Free PMC article.
-
PKC-ι promotes glioblastoma cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting BAD through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jun;1813(6):1190-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.007. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419810
-
In vitro enhancement of tumor cell radiosensitivity by a selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme: mechanistic considerations.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Nov 1;54(3):886-94. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03023-7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 12377342
-
Activation of caspase-3 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-1 signaling pathways in tamoxifen-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2000 Nov 1;60(21):5995-6000. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 11085519
-
Tamoxifen modulation of carboplatin cytotoxicity in a human U-138 glioma cell line.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1998 Jun;100(2):89-93. doi: 10.1016/s0303-8467(98)00004-3. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1998. PMID: 9746294
Cited by
-
Measuring the lactate-to-creatine ratio via 1H NMR spectroscopy can be used to noninvasively evaluate apoptosis in glioma cells after X-ray irradiation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Jun 15;23:27. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0092-2. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29946338 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Radiotherapy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 2;19(3):713. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030713. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29498642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans J, Wick W. Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and invasiveness of glioma cells: implications for radiotherapy of human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2744–2750. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
