Preparing Nursing Homes for the Future of Health Information Exchange
- PMID: 26171073
- PMCID: PMC4493328
- DOI: 10.4338/ACI-2014-12-RA-0113
Preparing Nursing Homes for the Future of Health Information Exchange
Abstract
Objective: Our purpose was to describe how we prepared 16 nursing homes (NHs) for health information exchange (HIE) implementation.
Background: NH HIE connecting internal and external stakeholders are in their infancy. U.S. initiatives are demonstrating HIE use to increase access and securely exchange personal health information to improve patient outcomes.
Method: To achieve our objectives we conducted readiness assessments, performed 32 hours of clinical observation and developed 6 use cases, and conducted semi-structured interviews with 230 participants during 68 site visits to validate use cases and explore HIE.
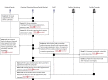
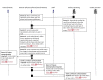
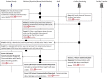
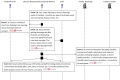
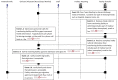
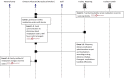
Results: All 16 NHs had technology available to support resident care. Resident care technologies were integrated much more with internal than external stakeholders. A wide range of technologies were accessible only during administrative office hours. Six non-emergent use cases most commonly communicated by NH staff were: 1) scheduling appointments, 2) Laboratory specimen drawing, 3) pharmacy orders and reconciliation, 4) social work discharge planning, 5) admissions and pre-admissions, and 6) pharmacy-medication reconciliation. Emerging themes from semi-structured interviews about use cases included: availability of information technology in clinical settings, accessibility of HIE at the point of care, and policies/procedures for sending/receiving secure personal health information.
Conclusion: We learned that every facility needed additional technological and human resources to build an HIE network. Also, use cases help clinical staff apply theoretical problems of HIE implementation and helps them think through the implications of using HIE to communicate about clinical care.
Keywords: Health information exchange; health information technology; long-term care; nursing home; utilization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring Health Information Exchange Implementation Using Qualitative Assessments of Nursing Home Leaders.Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2016 Oct 1;13(Fall):1f. eCollection 2016 fall. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2016. PMID: 27843423 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of a health information exchange into community pharmacy workflow.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2017 Sep-Oct;57(5):608-615. doi: 10.1016/j.japh.2017.05.009. Epub 2017 Jul 18. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2017. PMID: 28733155
-
A mixed-method service evaluation of health information exchange in England: technology acceptance and barriers and facilitators to adoption.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jul 25;21(1):737. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06771-z. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34303379 Free PMC article.
-
Health information exchanges--Unfulfilled promise as a data source for clinical research.Int J Med Inform. 2016 Mar;87:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Int J Med Inform. 2016. PMID: 26806706 Review.
-
Health information exchange in general practice care for people with intellectual disabilities--a qualitative review of the literature.Res Dev Disabil. 2014 Sep;35(9):1978-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.04.029. Epub 2014 May 24. Res Dev Disabil. 2014. PMID: 24864050 Review.
Cited by
-
Nursing Information Flow in Long-Term Care Facilities.Appl Clin Inform. 2018 Apr;9(2):275-284. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1642609. Epub 2018 May 2. Appl Clin Inform. 2018. PMID: 29719883 Free PMC article.
-
Multitasking during Medication Management in a Nursing Home: A Time Motion Study.Appl Clin Inform. 2024 Oct;15(5):877-888. doi: 10.1055/a-2379-7206. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Appl Clin Inform. 2024. PMID: 39102866
-
Information Needs of Skilled Nursing Facility Staff to Support Heart Failure Disease Management.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2021 Jan 25;2020:878-885. eCollection 2020. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2021. PMID: 33936463 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the concepts of a smart nursing home and its potential technology utilities that integrate medical services and are acceptable to stakeholders: a scoping review.BMC Geriatr. 2022 Oct 7;22(1):787. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03424-6. BMC Geriatr. 2022. PMID: 36207705 Free PMC article.
-
A national report of nursing home information technology: year 1 results.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2017 Jan;24(1):67-73. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocw051. Epub 2016 Apr 23. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2017. PMID: 27107444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention FastStats Homepage. http://wwwcdc gov/nchs/fastats/nursingh htm 2011 February 18
-
- Department of Health and Human Services. HealthIT.gov http://www healthit gov/HIE 2012 March 14;Available from: URL: http://www.healthit.gov/HIE
-
- Georgiou A, Marks A, Braithwaite J, Westbrook J. Gaps, Disconnections, and Discontinuities—The Role of Information Exchange in the Delivery of Quality Long-Term Care. The Gerontologist 2013; 53(5): 770-779. - PubMed
-
- Rouse M. TechTarget: Personal Health Information. http://searchhealthittechtarget com/definition/personal-health-information 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

