Reconstruction of Defects After Fournier Gangrene: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 26171090
- PMCID: PMC4447098
Reconstruction of Defects After Fournier Gangrene: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Reconstruction of scrotal defects after Fournier gangrene is often achieved with skin grafts or flaps, but there is no general consensus on the best method of reconstruction or how to approach the exposed testicle. We systematically reviewed the literature addressing methods of reconstruction of Fournier defects after debridement.
Methods: PubMed and Cochrane databases were searched from 1950 to 2013. Inclusion criteria were reconstruction for Fournier defects, patients 18 to 90 years old, and reconstructive complication rates reported as whole numbers or percentages. Exclusion criteria were studies focused on methods of debridement or other phases of care rather than reconstruction, studies with fewer than 5 male patients with Fournier defects, literature reviews, and articles not in English.
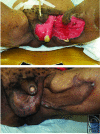
Results: The initial search yielded 982 studies, which was refined to 16 studies with a total pool of 425 patients. There were 25 (5.9%) patients with defects that healed by secondary intention, 44 (10.4%) with delayed primary closure, 36 (8.5%) with implantation of the testicle in a medial thigh pocket, 6 (1.4%) with loose wound approximation, 96 (22.6%) with skin grafts, 68 (16.0%) with scrotal advancement flaps, 128 (30.1%) with flaps, and 22 (5.2%) with flaps or skin grafts in combination with tissue adhesives. Four outcomes were evaluated: number of patients, defect size, method of reconstruction, and wound-healing complications.
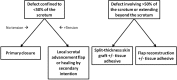
Conclusions: Most reconstructive techniques provide reliable coverage and protection of testicular function with an acceptable cosmetic result. There is no conclusive evidence to support flap coverage of exposed testes rather than skin graft. A reconstructive algorithm is proposed. Skin grafting or flap reconstruction is recommended for defects larger than 50% of the scrotum or extending beyond the scrotum, whereas scrotal advancement flap reconstruction or healing by secondary intention is best for defects confined to less than 50% of the scrotum that cannot be closed primarily without tension.
Keywords: Fournier gangrene; scrotal advancement flap; scrotal and perineal defects; skin graft; systematic review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fournier gangrene - would you KISS it?GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2023 Dec 11;12:Doc12. doi: 10.3205/iprs000182. eCollection 2023. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2023. PMID: 38111841 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of scrotal and perineal defects in Fournier's gangrene.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011 Apr;64(4):528-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2010.07.018. Epub 2010 Aug 24. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011. PMID: 20797927
-
SCROTAL RECONSTRUCTION WITH A PEDICLED GRACILIS MUSCLE FLAP AFTER DEBRIDEMENT OF FOURNIER'S GANGRENE: A CASE REPORT.East Afr Med J. 2013 Nov;90(11):375-8. East Afr Med J. 2013. PMID: 26862639
-
Crafting Contours: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrotal Reconstruction.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;14(2):223. doi: 10.3390/life14020223. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scrotal reconstruction and testicular prosthetics.Transl Androl Urol. 2017 Aug;6(4):710-721. doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.07.06. Transl Androl Urol. 2017. PMID: 28904904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pudendal flap-a good option for creating neo-scrotum after Fournier's gangrene: a case series.J Surg Case Rep. 2020 Nov 14;2020(11):rjaa414. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjaa414. eCollection 2020 Nov. J Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33224466 Free PMC article.
-
Neglected Fournier's Gangrene Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: A Rare Case Report.Case Rep Surg. 2016;2016:8461354. doi: 10.1155/2016/8461354. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Case Rep Surg. 2016. PMID: 27725892 Free PMC article.
-
Flaps in adult urethrocutaneous fistula repair: a report of two cases with the review of literature.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Apr 19;14(4):e236475. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236475. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33875497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fournier's Gangrene: Clinical Presentation of 13 Cases.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jan 28;24:548-555. doi: 10.12659/msm.905836. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29374769 Free PMC article.
-
Fournier's gangrene: a review of reconstructive options.Cent European J Urol. 2020;73(1):74-79. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2020.0060. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Cent European J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32395328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Erol B, Tuncel A, Hanci V, et al. Fournier's gangrene: overview of prognostic factors and definition of new prognostic parameter. Urology. 2010;75:1193–8. - PubMed
-
- Norton KS, Johnson LW, Perry T, Perry KH, Sehon JK, Zibari GB. Management of Fournier's gangrene: an eleven year retrospective analysis of early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment. Am Surg. 2002;68:709–13. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho JP, Hazan A, Cavalcanti AG, Favorito LA. Relation between the area affected by Fournier's gangrene and the type of reconstructive surgery used. A study with 80 patients. Int Braz J Urol. 2007;33:510–4. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnager AM, Mohite PN, Suthar M. Fournier's gangrene: a review of 110 cases for aetiology, predisposing conditions, microorganisms, and modalities for coverage of necrosed scrotum with bare testes. N Z Med J. 2008;121:46–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
