Biomarker detection for disease diagnosis using cost-effective microfluidic platforms
- PMID: 26171467
- PMCID: PMC4604043
- DOI: 10.1039/c5an00780a
Biomarker detection for disease diagnosis using cost-effective microfluidic platforms
Abstract
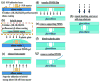
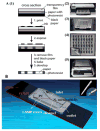
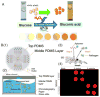
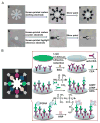
Early and timely detection of disease biomarkers can prevent the spread of infectious diseases, and drastically decrease the death rate of people suffering from different diseases such as cancer and infectious diseases. Because conventional diagnostic methods have limited application in low-resource settings due to the use of bulky and expensive instrumentation, simple and low-cost point-of-care diagnostic devices for timely and early biomarker diagnosis is the need of the hour, especially in rural areas and developing nations. The microfluidics technology possesses remarkable features for simple, low-cost, and rapid disease diagnosis. There have been significant advances in the development of microfluidic platforms for biomarker detection of diseases. This article reviews recent advances in biomarker detection using cost-effective microfluidic devices for disease diagnosis, with the emphasis on infectious disease and cancer diagnosis in low-resource settings. This review first introduces different microfluidic platforms (e.g. polymer and paper-based microfluidics) used for disease diagnosis, with a brief description of their common fabrication techniques. Then, it highlights various detection strategies for disease biomarker detection using microfluidic platforms, including colorimetric, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, electrochemiluminescence (ECL), and electrochemical detection. Finally, it discusses the current limitations of microfluidic devices for disease biomarker detection and future prospects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarker Detection in Early Diagnosis of Cancer: Recent Achievements in Point-of-Care Devices Based on Paper Microfluidics.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;13(3):387. doi: 10.3390/bios13030387. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects of Microfluidic Technology in Nucleic Acid Detection Approaches.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 May 27;13(6):584. doi: 10.3390/bios13060584. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in non-optical microfluidic platforms for bioparticle detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2023 Feb 15;222:114944. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114944. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023. PMID: 36470061 Review.
-
Low-cost bioanalysis on paper-based and its hybrid microfluidic platforms.Talanta. 2015 Dec 1;145:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.068. Epub 2015 May 6. Talanta. 2015. PMID: 26459442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics-based strategies for molecular diagnostics of infectious diseases.Mil Med Res. 2022 Mar 18;9(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00374-3. Mil Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35300739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simple Approach for Fluorescence Signal Amplification Utilizing a Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Based Polymer Structure in a Microchannel.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 17;6(12):8340-8345. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00057. eCollection 2021 Mar 30. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33817494 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Lateral Flow Device for Flow Control with Blood Separation and Biosensing.Micromachines (Basel). 2017;8(12):367. doi: 10.3390/mi8120367. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30345108 Free PMC article.
-
Lab-on-a-Chip Devices for Point-of-Care Medical Diagnostics.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022;179:247-265. doi: 10.1007/10_2020_127. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 32435872 Review.
-
Spatially Resolved Protein Binding Kinetics Analysis in Microfluidic Photonic Crystal Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 16;23(12):5637. doi: 10.3390/s23125637. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37420803 Free PMC article.
-
A microfluidic fully paper-based analytical device integrated with loop-mediated isothermal amplification and nano-biosensors for rapid, sensitive, and specific quantitative detection of infectious diseases.Lab Chip. 2022 Nov 22;22(23):4693-4704. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00834c. Lab Chip. 2022. PMID: 36349548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biomedical F. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Hung LY, Wu HW, Hsieh K, Lee GB. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2014;16:941–963.
-
- Adamczyk B, Tharmalingam T, Rudd PM. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects. 2012;1820:1347–1353. - PubMed
-
- Luo X, Davis JJ. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:5944–5962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

