Low-dose oxytocin delivered intranasally with Breath Powered device affects social-cognitive behavior: a randomized four-way crossover trial with nasal cavity dimension assessment
- PMID: 26171983
- PMCID: PMC5068727
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2015.93
Low-dose oxytocin delivered intranasally with Breath Powered device affects social-cognitive behavior: a randomized four-way crossover trial with nasal cavity dimension assessment
Abstract
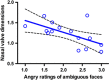
Despite the promise of intranasal oxytocin (OT) for modulating social behavior, recent work has provided mixed results. This may relate to suboptimal drug deposition achieved with conventional nasal sprays, inter-individual differences in nasal physiology and a poor understanding of how intranasal OT is delivered to the brain in humans. Delivering OT using a novel 'Breath Powered' nasal device previously shown to enhance deposition in intranasal sites targeted for nose-to-brain transport, we evaluated dose-dependent effects on social cognition, compared response with intravenous (IV) administration of OT, and assessed nasal cavity dimensions using acoustic rhinometry. We adopted a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, crossover design, with 16 healthy male adults completing four single-dose treatments (intranasal 8 IU (international units) or 24 IU OT, 1 IU OT IV and placebo). The primary outcome was social cognition measured by emotional ratings of facial images. Secondary outcomes included the pharmacokinetics of OT, vasopressin and cortisol in blood and the association between nasal cavity dimensions and emotional ratings. Despite the fact that all the treatments produced similar plasma OT increases compared with placebo, there was a main effect of treatment on anger ratings of emotionally ambiguous faces. Pairwise comparisons revealed decreased ratings after 8 IU OT in comparison to both placebo and 24 IU OT. In addition, there was an inverse relationship between nasal valve dimensions and anger ratings of ambiguous faces after 8-IU OT treatment. These findings provide support for a direct nose-to-brain effect, independent of blood absorption, of low-dose OT delivered from a Breath Powered device.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01983514.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dose-dependent social-cognitive effects of intranasal oxytocin delivered with novel Breath Powered device in adults with autism spectrum disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind crossover trial.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 May 23;7(5):e1136. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.103. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28534875 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Low dose intranasal oxytocin delivered with Breath Powered device dampens amygdala response to emotional stimuli: A peripheral effect-controlled within-subjects randomized dose-response fMRI trial.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016 Jul;69:180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27107209 Clinical Trial.
-
Low-dose intranasal oxytocin delivered with Breath Powered device modulates pupil diameter and amygdala activity: a randomized controlled pupillometry and fMRI study.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jan;44(2):306-313. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0241-3. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30323359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intranasal oxytocin effects on social cognition: a critique.Brain Res. 2014 Sep 11;1580:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24239931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do delivery routes of intranasally administered oxytocin account for observed effects on social cognition and behavior? A two-level model.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Feb;49:182-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25526824 Review.
Cited by
-
Tri-Phasic Model ofOxytocin (TRIO): A systematic conceptual review of oxytocin-related ERP research.Biol Psychol. 2020 Jul;154:107917. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2020.107917. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Biol Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32512020 Free PMC article.
-
Sniffing oxytocin: Nose to brain or nose to blood?Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jul;28(7):3083-3091. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02075-2. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37185959 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Central Oxytocin Transport: Known Realms and Uncharted Territories.Neuroscientist. 2025 Jun;31(3):234-261. doi: 10.1177/10738584241268754. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Neuroscientist. 2025. PMID: 39113465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Role of Oxytocin, Cortisol, and Testosterone in Facial Emotional Processing.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 15;10(12):1334. doi: 10.3390/biology10121334. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal Dynamics of Intranasal Oxytocin in Human Brain Electrophysiology.Cereb Cortex. 2022 Jul 12;32(14):3110-3126. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhab404. Cereb Cortex. 2022. PMID: 34979544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guastella AJ, MacLeod C. A critical review of the influence of oxytocin nasal spray on social cognition in humans: evidence and future directions. Horm Behav. 2012;61:410–418. - PubMed
-
- Meyer-Lindenberg A, Domes G, Kirsch P, Heinrichs M. Oxytocin and vasopressin in the human brain: social neuropeptides for translational medicine. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:524–538. - PubMed
-
- Striepens N, Kendrick KM, Maier W, Hurlemann R. Prosocial effects of oxytocin and clinical evidence for its therapeutic potential. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2011;32:426–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

