Isotonic Glycerol and Sodium Hyaluronate Containing Artificial Tear Decreases Conjunctivochalasis after One and Three Months: A Self-Controlled, Unmasked Study
- PMID: 26172053
- PMCID: PMC4501551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132656
Isotonic Glycerol and Sodium Hyaluronate Containing Artificial Tear Decreases Conjunctivochalasis after One and Three Months: A Self-Controlled, Unmasked Study
Abstract
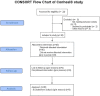
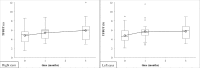
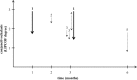
Dry eye complaints are ranked as the most frequent symptoms of patients visiting ophthalmologists. Conjunctivochalasis is a common dry eye disorder, which can cause an unstable tear film and ocular discomfort. The severe conjunctivochalasis characterized by high LId-Parallel COnjunctival Folds (LIPCOF) degree usually requires surgical intervention, where a conservative therapy would be highly desirable. Here we examined the efficacy of a preservative-free, inorganic salt-free unit-dose artificial tear, called Conheal containing isotonic glycerol and 0.015% sodium hyaluronate in a prospective, unmasked, self-controlled study involving 20 patients. The regular use of the glycerol/hyaluronate artificial tear in three months caused a significant improvement in the recorded parameters. Conjunctivochalasis decreased from a mean LIPCOF degree of 2.9 ± 0.4 on both eyes to 1.4 ± 0.6 on the right (median decrease of -2 points, 95% CI from -2.0 to -1.0), and to 1.4 ± 0.7 on the left eye (median decrease of -1 points, 95% CI from -2.0 to -1.0) (p<0.001 for both sides). The tear film breakup time (TFBUT) lengthened from 4.8 ± 1.9 seconds on both eyes to 5.9 ± 2.3 seconds (mean increase of 1.1 seconds, 95% CI from 0.2 to 2.0) and 5.7 ± 1.8 seconds (mean increase of 0.9 seconds, 95% CI from 0.3 to 1.5) on the right and left eyes, respectively (p(right eyes) = 0.020, p(left eyes) = 0.004). The corneal lissamine staining (Oxford Scheme grade) was reduced from 1.3 ± 0.6 on the right and 1.4 ± 0.6 on the left eye significantly (p<0.001) to 0.3 ± 0.4 and 0.2 ± 0.4 on the right and the left eyes. The Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire score indicating the subjective complaints of the patients also decreased from a mean value of 36.2 ± 25.3 to 15.6 ± 16.7 (p<0.001). In this study, the artificial tear, Conheal decreased the grade of the conjunctivochalasis significantly after one month of regular use already, from the LIPCOF degree 3, considered as indication of conjunctival surgery, to a LIPCOF degree 2 or lower requiring a conservative therapy. Our results raise the possibility that vision-related quality of life can be significantly improved by conservative therapies even in severe conjunctivochalasis.
Trial registration: Controlled-Trials.com ISRCTN81112701 http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN81112701.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical impact of conjunctivochalasis on the ocular surface.Cornea. 2005 Nov;24(8 Suppl):S24-S31. doi: 10.1097/01.ico.0000178740.14212.1a. Cornea. 2005. PMID: 16227820 Clinical Trial.
-
Can the optimum artificial tear treatment for dry eye disease be predicted from presenting signs and symptoms?Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2018 Feb;41(1):60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2018. PMID: 28811095 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a hyaluronic acid and carboxymethylcellulose ophthalmic solution on ocular comfort and tear-film instability after cataract surgery.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015 Aug;41(8):1699-704. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2014.12.056. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015. PMID: 26432128 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of Lacrycon® eye drops for the treatment of dry eye syndrome.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019 Jun;42(6):642-654. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2018.08.008. Epub 2019 Mar 28. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019. PMID: 30929965
-
Surgery of the conjunctiva.Dev Ophthalmol. 2008;41:138-158. doi: 10.1159/000131086. Dev Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18453766 Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanism of Qijing Mingmu decoction on cellular senescence of conjunctivochalasis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Aug 29;23(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04138-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37644481 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid and Galacto-Xyloglucan Eyedrop Efficacy in Young-Adult Oral Contraceptive Users of Childbearing Age.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 30;11(15):4458. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154458. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956073 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular surface involvement and histopathologic changes in the acute stage of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a cross-sectional study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul 3;23(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-03052-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37400766 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic benefits of glycerol in dry eye disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 15;11:1531670. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1531670. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39882517 Free PMC article.
-
The role of elastic fibers in pathogenesis of conjunctivochalasis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2017 Sep 18;10(9):1465-1473. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2017.09.21. eCollection 2017. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28944209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith JA, Albeitz J, Begley C, Caffery B, Nichols K, Schaumberg D, et al. The epidemiology of dry eye disease: report of the Epidemiology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop. Ocul Surf. 2007;5(2):93–107. - PubMed
-
- Petricek I, Prost M, Popova A. The differential diagnosis of red eye: a survey of medical practitioners from Eastern Europe and the Middle East. Ophthalmologica. 2006;220(4):229–237. - PubMed
-
- Schaumberg DA, Sullivan DA, Dana MR. Epidemiology of dry eye syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;506:989–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

