eIF3 controls cell size independently of S6K1-activity
- PMID: 26172298
- PMCID: PMC4695191
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4458
eIF3 controls cell size independently of S6K1-activity
Abstract
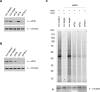
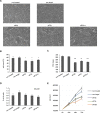
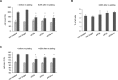
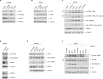
All multicellular organisms require a life-long regulation of the number and the size of cells, which build up their organs. mTOR acts as a signaling nodule for the regulation of protein synthesis and growth. To activate the translational cascade, mTOR phosphorylates S6 kinase (S6K1), which is liberated from the eIF3-complex and mobilized for activation of its downstream targets. How S6K1 regulates cell size remains unclear. Here, we challenged cell size control through S6K1 by specifically depleting its binding partner eIF3 in normal and transformed cell lines. We show that loss of eIF3 leads to a massive reduction of cell size and cell number accompanied with an unexpected increase in S6K1-activity. The hyperactive S6K1-signaling was rapamycin-sensitive, suggesting an upstream mTOR-regulation. A selective S6K1 inhibitor (PF-4708671) was unable to interfere with the reduced size, despite efficiently inhibiting S6K1-activity. Restoration of eIF3 expression recovered size defects, without affecting the p-S6 levels. We further show that two, yet uncharacterized, cancer-associated mutations in the eIF3-complex, have the capacity to recover from reduced size phenotype, suggesting a possible role for eIF3 in regulating cancer cell size. Collectively, our results uncover a role for eIF3-complex in maintenance of normal and neoplastic cell size - independent of S6K1-signaling.
Keywords: S6K; cancer; cell size; eIF3; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

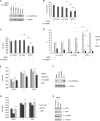
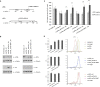
Similar articles
-
Control of Paip1-eukayrotic translation initiation factor 3 interaction by amino acids through S6 kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;34(6):1046-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01079-13. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24396066 Free PMC article.
-
p70 S6K1 nuclear localization depends on its mTOR-mediated phosphorylation at T389, but not on its kinase activity towards S6.Amino Acids. 2012 Jun;42(6):2251-6. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0965-4. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 21710263
-
S6K1 plays a key role in glial transformation.Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 15;68(16):6516-23. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6188. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18701474 Free PMC article.
-
eIF3: a connecTOR of S6K1 to the translation preinitiation complex.Mol Cell. 2005 Dec 9;20(5):655-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.11.016. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16337588 Review.
-
The S6K protein family in health and disease.Life Sci. 2015 Jun 15;131:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25818187 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of TFEB Drives a Pleiotropic Neurotrophic Effect and Prevents Parkinson's Disease-Related Neurodegeneration.Mol Ther. 2018 Jun 6;26(6):1552-1567. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.022. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29628303 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal Protein S6: A Potential Therapeutic Target against Cancer?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 21;23(1):48. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010048. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced neuronal size and mTOR pathway activity in the Mecp2 A140V Rett syndrome mouse model.F1000Res. 2016 Sep 8;5:2269. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.8156.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27781091 Free PMC article.
-
Superior efficacy of co-treatment with the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 and histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A against NSCLC.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60169-60180. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11109. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27507059 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key regulators in prostate cancer from gene expression datasets of patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 11;9(1):16420. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52896-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31712650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd AC. The regulation of cell size. Cell. 2013;154:1194–1205. - PubMed
-
- Conlon I, Raff M. Size control in animal development. Cell. 1999;96:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Rosenwald IB. The role of translation in neoplastic transformation from a pathologist's point of view. Oncogene. 2004;23:3230–3247. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Pan X, Hershey JW. Individual overexpression of five subunits of human translation initiation factor eIF3 promotes malignant transformation of immortal fibroblast cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5790–5800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

