IGF-1 deficiency impairs neurovascular coupling in mice: implications for cerebromicrovascular aging
- PMID: 26172407
- PMCID: PMC4693458
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12372
IGF-1 deficiency impairs neurovascular coupling in mice: implications for cerebromicrovascular aging
Abstract
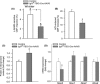
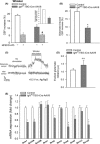
Aging is associated with marked deficiency in circulating IGF-1, which has been shown to contribute to age-related cognitive decline. Impairment of moment-to-moment adjustment of cerebral blood flow (CBF) via neurovascular coupling is thought to play a critical role in the genesis of age-related cognitive impairment. To establish the link between IGF-1 deficiency and cerebromicrovascular impairment, neurovascular coupling mechanisms were studied in a novel mouse model of IGF-1 deficiency (Igf1(f/f) -TBG-Cre-AAV8) and accelerated vascular aging. We found that IGF-1-deficient mice exhibit neurovascular uncoupling and show a deficit in hippocampal-dependent spatial memory test, mimicking the aging phenotype. IGF-1 deficiency significantly impaired cerebromicrovascular endothelial function decreasing NO mediation of neurovascular coupling. IGF-1 deficiency also impaired glutamate-mediated CBF responses, likely due to dysregulation of astrocytic expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors and impairing mediation of CBF responses by eicosanoid gliotransmitters. Collectively, we demonstrate that IGF-1 deficiency promotes cerebromicrovascular dysfunction and neurovascular uncoupling mimicking the aging phenotype, which are likely to contribute to cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Insulin-like growth factor-1; arachidonic acid metabolites; astrocyte; endothelial dysfunction; functional hyperemia; neurovascular uncoupling; nitric oxide; somatomedin C; vascular aging; vascular cognitive impairment.
© 2015 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impaired neurovascular coupling in aging and Alzheimer's disease: Contribution of astrocyte dysfunction and endothelial impairment to cognitive decline.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Aug;94:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.11.004. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 27845201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial deficiency of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) impairs neurovascular coupling responses in mice, mimicking aspects of the brain aging phenotype.Geroscience. 2021 Oct;43(5):2387-2394. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00405-2. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 34383203 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating IGF-1 deficiency exacerbates hypertension-induced microvascular rarefaction in the mouse hippocampus and retrosplenial cortex: implications for cerebromicrovascular and brain aging.Age (Dordr). 2016 Aug;38(4):273-289. doi: 10.1007/s11357-016-9931-0. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Age (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 27613724 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-1 deficiency impairs cerebral myogenic autoregulation in hypertensive mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Dec;34(12):1887-97. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.156. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 25248835 Free PMC article.
-
Functional vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: mechanisms and consequences of cerebral autoregulatory dysfunction, endothelial impairment, and neurovascular uncoupling in aging.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):H1-H20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00581.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27793855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging retinal microvascular manifestations of carotid artery disease in older adults: from diagnosis of ocular complications to understanding microvascular contributions to cognitive impairment.Geroscience. 2021 Aug;43(4):1703-1723. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00392-4. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 34100219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and the Neurovascular Unit.Life (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;11(8):767. doi: 10.3390/life11080767. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension-induced synapse loss and impairment in synaptic plasticity in the mouse hippocampus mimics the aging phenotype: implications for the pathogenesis of vascular cognitive impairment.Geroscience. 2017 Aug;39(4):385-406. doi: 10.1007/s11357-017-9981-y. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Geroscience. 2017. PMID: 28664509 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological or genetic depletion of senescent astrocytes prevents whole brain irradiation-induced impairment of neurovascular coupling responses protecting cognitive function in mice.Geroscience. 2020 Apr;42(2):409-428. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00154-8. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Geroscience. 2020. PMID: 31960269 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific mechanisms in vascular aging: exploring cellular and molecular pathways in the pathogenesis of age-related cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.Geroscience. 2025 Feb;47(1):301-337. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01489-2. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39754010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey‐Downs LC, Mitschelen M, Sosnowska D, Toth P, Pinto JT, Ballabh P, Valcarcel‐Ares MN, Farley J, Koller A, Henthorn JC, Bass C, Sonntag WE, Ungvari Z, Csiszar A (2012) Liver‐specific knockdown of IGF‐1 decreases vascular oxidative stress resistance by impairing the Nrf2‐dependent antioxidant response: a novel model of vascular aging. J. Gerontol. Biol. Med. Sci. 67, 313–329. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berenbaum F, Thomas G, Poiraudeau S, Bereziat G, Corvol MT, Masliah J (1994) Insulin‐like growth factors counteract the effect of interleukin 1 beta on type II phospholipase A2 expression and arachidonic acid release by rabbit articular chondrocytes. FEBS Lett. 340, 51–55. - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Dishman E, Karara A, Falck JR (1991) Cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase: stereochemical characterization of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Methods Enzymol. 206, 441–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

