Identification of a Novel Regulatory Mechanism of Nutrient Transport Controlled by TORC1-Npr1-Amu1/Par32
- PMID: 26172854
- PMCID: PMC4501750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005382
Identification of a Novel Regulatory Mechanism of Nutrient Transport Controlled by TORC1-Npr1-Amu1/Par32
Abstract
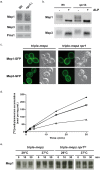
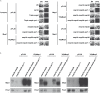
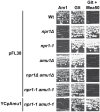
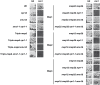
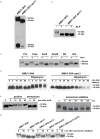
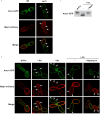
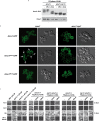
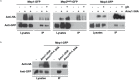
Fine-tuning the plasma-membrane permeability to essential nutrients is fundamental to cell growth optimization. Nutritional signals including nitrogen availability are integrated by the TORC1 complex which notably regulates arrestin-mediated endocytosis of amino-acid transporters. Ammonium is a ubiquitous compound playing key physiological roles in many, if not all, organisms. In yeast, it is a preferred nitrogen source transported by three Mep proteins which are orthologues of the mammalian Rhesus factors. By combining genetic, kinetic, biochemical and cell microscopy analyses, the current study reveals a novel mechanism enabling TORC1 to regulate the inherent activity of ammonium transport proteins, independently of arrestin-mediated endocytosis, identifying the still functional orphan Amu1/Par32 as a selective regulator intermediate. We show that, under poor nitrogen supply, the TORC1 effector kinase' Npr1' promotes phosphorylation of Amu1/Par32 which appears mainly cytosolic while ammonium transport proteins are active. Upon preferred nitrogen supplementation, like glutamine or ammonium addition, TORC1 upregulation enables Npr1 inhibition and Amu1/Par32 dephosphorylation. In these conditions, as in Npr1-lacking cells, hypophosphorylated Amu1/Par32 accumulates at the cell surface and mediates the inhibition of specific ammonium transport proteins. We show that the integrity of a conserved repeated motif of Amu1/Par32 is required for the interaction with these transport proteins. This study underscores the diversity of strategies enabling TORC1-Npr1 to selectively monitor cell permeability to nutrients by discriminating between transporters to be degraded or transiently inactivated and kept stable at the plasma membrane. This study further identifies the function of Amu1/Par32 in acute control of ammonium transport in response to variations in nitrogen availability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Marini AM, Urrestarazu A, Beauwens R, Andre B. The Rh (rhesus) blood group polypeptides are related to NH4+ transporters. Trends Biochem. 1997;22: 460–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

