POLD1 Germline Mutations in Patients Initially Diagnosed with Werner Syndrome
- PMID: 26172944
- PMCID: PMC4684254
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22833
POLD1 Germline Mutations in Patients Initially Diagnosed with Werner Syndrome
Abstract
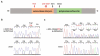
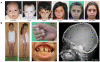
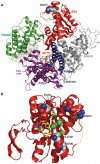
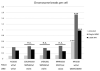
Segmental progeroid syndromes are rare, heterogeneous disorders characterized by signs of premature aging affecting more than one tissue or organ. A prototypic example is the Werner syndrome (WS), caused by biallelic germline mutations in the Werner helicase gene (WRN). While heterozygous lamin A/C (LMNA) mutations are found in a few nonclassical cases of WS, another 10%-15% of patients initially diagnosed with WS do not have mutations in WRN or LMNA. Germline POLD1 mutations were recently reported in five patients with another segmental progeroid disorder: mandibular hypoplasia, deafness, progeroid features syndrome. Here, we describe eight additional patients with heterozygous POLD1 mutations, thereby substantially expanding the characterization of this new example of segmental progeroid disorders. First, we identified POLD1 mutations in patients initially diagnosed with WS. Second, we describe POLD1 mutation carriers without clinically relevant hearing impairment or mandibular underdevelopment, both previously thought to represent obligate diagnostic features. These patients also exhibit a lower incidence of metabolic abnormalities and joint contractures. Third, we document postnatal short stature and premature greying/loss of hair in POLD1 mutation carriers. We conclude that POLD1 germline mutations can result in a variably expressed and probably underdiagnosed segmental progeroid syndrome.
Keywords: POLD1; Werner syndrome; deafness; mandibular hypoplasia; progeroid features (MDP) syndrome.
© 2015 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwal AK, Fryns JP, Auchus RJ, Garg A. Zinc metalloproteinase, ZMPSTE24, is mutated in mandibuloacral dysplasia. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:1995–2001. - PubMed
-
- Barrios Sanjuanelo A, Munoz Otero C. Atypical Werner syndrome: atypical progeroid syndrome: a case report. An Pediatr (Barc) 2010;73:94–97. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Lee L, Kudlow BA, Dos Santos HG, Sletvold O, Shafeghati Y, Botha EG, Garg A, Hanson NB, Martin GM, Mian IS, Kennedy BK, Oshima J. LMNA mutations in atypical Werner’s syndrome. Lancet. 2003;362:440–445. - PubMed
-
- Hisama FM, Lessel D, Leistritz D, Friedrich K, McBride KL, Pastore MT, Gottesman GS, Saha B, Martin GM, Kubisch C, Oshima J. Coronary artery disease in a Werner syndrome-like form of progeria characterized by low levels of progerin, a splice variant of lamin A. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A:3002–3006. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

