Fecal detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis
- PMID: 26173688
- PMCID: PMC5001496
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-015-2425-7
Fecal detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis
Abstract
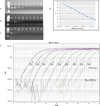
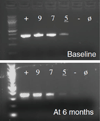
Bacteroides fragilis is a common colonic symbiote of which one subtype, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF), causes inflammatory diarrhea. However, asymptomatic ETBF colonization is common. Through its primary virulence factor, B. fragilis toxin (BFT), ETBF causes asymptomatic, chronic colitis in C57BL/6 mice and increased colon tumorigenesis in multiple intestinal neoplasia mice. Human studies suggest an association between ETBF infection, inflammatory bowel disease, and colon cancer. Additional studies on ETBF epidemiology are, therefore, crucial. The goal of this study is to develop a reliable fecal diagnostic for ETBF. To develop a sensitive assay for ETBF, we tested multiple protocols on mouse stools spiked with serially diluted ETBF. Each assay was based on either touchdown or quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and used primers targeted to bft to detect ETBF. Using touchdown PCR or qPCR, the mean ETBF detection limit was 1.55 × 10(6) colony-forming units (CFU)/g stool and 1.33 × 10(4) CFU/g stool, respectively. Augmentation of Bacteroides spp. growth in fecal samples using PYGB (Peptone Yeast Glucose with Bile) broth enhanced ETBF detection to 2.93 × 10(2) CFU/g stool using the touchdown PCR method and 2.63 × 10(2) CFU/g stool using the qPCR method. Fecal testing using combined culture-based amplification and bft touchdown PCR is a sensitive assay for the detection of ETBF colonization and should be useful in studying the role of ETBF colonization in intestinal diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. We conclude that touchdown PCR with culture-based amplification may be the optimal ETBF detection strategy, as it performs as well as qPCR with culture-based amplification, but is a less expensive technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening for enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in stool samples.Anaerobe. 2016 Aug;40:50-3. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 7. Anaerobe. 2016. PMID: 27166180
-
Induction of persistent colitis by a human commensal, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1708-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00814-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19188353 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis by PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Oct;35(10):2482-6. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.10.2482-2486.1997. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9316893 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: a rogue among symbiotes.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009 Apr;22(2):349-69, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00053-08. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19366918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis as a factor in diarrhea].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002 Jan;36(1):99-103. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002. PMID: 12476774 Review. Turkish.
Cited by
-
Gastrointestinal Pathobionts in Pediatric Crohn's Disease Patients.Int J Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;2018:9203908. doi: 10.1155/2018/9203908. eCollection 2018. Int J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30123276 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiome and colorectal cancer: a review of bacterial pathogenesis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018 Aug;9(4):769-777. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2018.04.07. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30151274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colonization with enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis is associated with early-stage colorectal neoplasia.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0171602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171602. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28151975 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Sample Extraction and Library Construction for Shotgun Metagenomics.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020 Jun 3;14:1177932220915459. doi: 10.1177/1177932220915459. eCollection 2020. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020. PMID: 32546984 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Detection, and Characterization of Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in Clinical Samples.Open Microbiol J. 2016 Apr 14;10:57-63. doi: 10.2174/1874285801610010057. eCollection 2016. Open Microbiol J. 2016. PMID: 27335618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arumugam M, Raes J, Pelletier E, Le Paslier D, Yamada T, Mende DR, Fernandes GR, Tap J, Bruls T, Batto JM, Bertalan M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Fernandez L, Gautier L, Hansen T, Hattori M, Hayashi T, Kleerebezem M, Kurokawa K, Leclerc M, Levenez F, Manichanh C, Nielsen HB, Nielsen T, Pons N, Poulain J, Qin J, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Tims S, Torrents D, Ugarte E, Zoetendal EG, Wang J, Guarner F, Pedersen O, de Vos WM, Brunak S, Doré J, MetaHIT Consortium. Antolín M, Artiguenave F, Blottiere HM, Almeida M, Brechot C, Cara C, Chervaux C, Cultrone A, Delorme C, Denariaz G, Dervyn R, Foerstner KU, Friss C, van de Guchte M, Guedon E, Haimet F, Huber W, van Hylckama-Vlieg J, Jamet A, Juste C, Kaci G, Knol J, Lakhdari O, Layec S, Le Roux K, Maguin E, Mérieux A, Melo Minardi R, M’rini C, Muller J, Oozeer R, Parkhill J, Renault P, Rescigno M, Sanchez N, Sunagawa S, Torrejon A, Turner K, Vandemeulebrouck G, Varela E, Winogradsky Y, Zeller G, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Bork P. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2011;473:174–180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Namavar F, Theunissen EBM, Verweij-Van Vught AMJJ, Peerbooms PGH, Bal M, Hoitsma HFW, Maclaren DM. Epidemiology of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the colonic flora in 10 patients with colonic cancer. J Med Microbiol. 1989;29:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Sack RB, Myers LL, Almeido-Hill J, Shoop DS, Bradbury WC, Reid R, Santosham M. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: epidemiologic studies of its role as a human diarrhoeal pathogen. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1992;10:4–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

