The Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α Augments Bacterial Killing through Sustained Oxidant Production
- PMID: 26173697
- PMCID: PMC4502229
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00705-15
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α Augments Bacterial Killing through Sustained Oxidant Production
Abstract
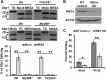
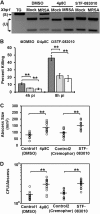
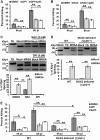
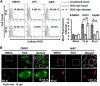
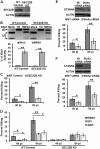
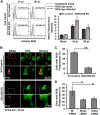
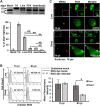
Bacterial infection can trigger cellular stress programs, such as the unfolded protein response (UPR), which occurs when misfolded proteins accumulate within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here, we used the human pathogen methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as an infection model to probe how ER stress promotes antimicrobial function. MRSA infection activated the most highly conserved unfolded protein response sensor, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), which was necessary for robust bacterial killing in vitro and in vivo. The macrophage IRE1-dependent bactericidal activity required reactive oxygen species (ROS). Viable MRSA cells excluded ROS from the nascent phagosome and strongly triggered IRE1 activation, leading to sustained generation of ROS that were largely Nox2 independent. In contrast, dead MRSA showed early colocalization with ROS but was a poor activator of IRE1 and did not trigger sustained ROS generation. The global ROS stimulated by IRE1 signaling was necessary, but not sufficient, for MRSA killing, which also required the ER resident SNARE Sec22B for accumulation of ROS in the phagosomal compartment. Taken together, these results suggest that IRE1-mediated persistent ROS generation might act as a fail-safe mechanism to kill bacterial pathogens that evade the initial macrophage oxidative burst.
Importance: Cellular stress programs have been implicated as important components of the innate immune response to infection. The role of the IRE1 pathway of the ER stress response in immune secretory functions, such as antibody production, is well established, but its contribution to innate immunity is less well defined. Here, we show that infection of macrophages with viable MRSA induces IRE1 activation, leading to bacterial killing. IRE1-dependent bactericidal activity required generation of reactive oxygen species in a sustained manner over hours of infection. The SNARE protein Sec22B, which was previously demonstrated to control ER-phagosome trafficking, was dispensable for IRE1-driven global ROS production but necessary for late ROS accumulation in bacteria-containing phagosomes. Our study highlights a key role for IRE1 in promoting macrophage bactericidal capacity and reveals a fail-safe mechanism that leads to the concentration of antimicrobial effector molecules in the macrophage phagosome.
Copyright © 2015 Abuaita et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondria-Derived Vesicles Deliver Antimicrobial Reactive Oxygen Species to Control Phagosome-Localized Staphylococcus aureus.Cell Host Microbe. 2018 Nov 14;24(5):625-636.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Host Microbe. 2018. PMID: 30449314 Free PMC article.
-
HCV induces transforming growth factor β1 through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 1;6:22487. doi: 10.1038/srep22487. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26927933 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation potentiates the infectivity of influenza A virus by regulating the host redox state.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 1;135:293-305. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.03.021. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30905731
-
IRE1: ER stress sensor and cell fate executor.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;23(11):547-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.06.005. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23880584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the ER stress sensor IRE1 in cardiovascular diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Feb;480(2):683-691. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05014-z. Epub 2024 May 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38717685 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting IRE1α-endonuclease activity decreases tumor burden in a mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma.Elife. 2020 Oct 26;9:e55865. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55865. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33103995 Free PMC article.
-
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) causes sepsis-associated acute lung injury via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 27;7:41363. doi: 10.1038/srep41363. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28128330 Free PMC article.
-
LACC1 Required for NOD2-Induced, ER Stress-Mediated Innate Immune Outcomes in Human Macrophages and LACC1 Risk Variants Modulate These Outcomes.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 24;29(13):4525-4539.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.105. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31875558 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and immunomodulator activities of virgin coconut oil (VCO) against Staphylococcus aureus.Heliyon. 2019 Oct 20;5(10):e02612. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02612. eCollection 2019 Oct. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31673647 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-Canonical Role for IRE1α Links ER and Mitochondria as Key Regulators of Astrocyte Dysfunction: Implications in Methamphetamine use and HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 17;16:906651. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.906651. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35784841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Kaufman RJ. 2002. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev 16:452–466. doi:10.1101/gad.964702. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- SRA/SRP034661
- SRA/SRP036144
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

