Age-dependency of sevoflurane-induced electroencephalogram dynamics in children
- PMID: 26174303
- PMCID: PMC4501917
- DOI: 10.1093/bja/aev114
Age-dependency of sevoflurane-induced electroencephalogram dynamics in children
Abstract
Background: General anaesthesia induces highly structured oscillations in the electroencephalogram (EEG) in adults, but the anaesthesia-induced EEG in paediatric patients is less understood. Neural circuits undergo structural and functional transformations during development that might be reflected in anaesthesia-induced EEG oscillations. We therefore investigated age-related changes in the EEG during sevoflurane general anaesthesia in paediatric patients.
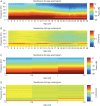
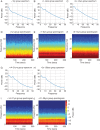
Methods: We analysed the EEG recorded during routine care of patients between 0 and 28 yr of age (n=54), using power spectral and coherence methods. The power spectrum quantifies the energy in the EEG at each frequency, while the coherence measures the frequency-dependent correlation or synchronization between EEG signals at different scalp locations. We characterized the EEG as a function of age and within 5 age groups: <1 yr old (n=4), 1-6 yr old (n=12), >6-14 yr old (n=14), >14-21 yr old (n=11), >21-28 yr old (n=13).
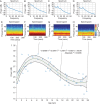
Results: EEG power significantly increased from infancy through ∼6 yr, subsequently declining to a plateau at approximately 21 yr. Alpha (8-13 Hz) coherence, a prominent EEG feature associated with sevoflurane-induced unconsciousness in adults, is absent in patients <1 yr.
Conclusions: Sevoflurane-induced EEG dynamics in children vary significantly as a function of age. These age-related dynamics likely reflect ongoing development within brain circuits that are modulated by sevoflurane. These readily observed paediatric-specific EEG signatures could be used to improve brain state monitoring in children receiving general anaesthesia.
Keywords: electroencephalography; pediatric; sevoflurane.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Journal of Anaesthesia. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Lin EP, Soriano SG, Loepke AW. Anesthetic neurotoxicity. Anesthesiol Clin 2014; 32: 133–55 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

