Anisakis pegreffii Larvae in Sea Eels (Astroconger myriaster) from the South Sea, Republic of Korea
- PMID: 26174831
- PMCID: PMC4510688
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2015.53.3.349
Anisakis pegreffii Larvae in Sea Eels (Astroconger myriaster) from the South Sea, Republic of Korea
Abstract
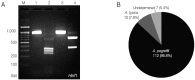
Anisakis simplex sensu stricto (s.s.), Anisakis pegreffii, Anisakis berlandi (=A. simplex sp. C), and Anisakis typica are the 4 major species of Anisakis type I larvae. In the Republic of Korea (Korea), A. pegreffii, A. berlandi, and A. typica larvae in fish hosts has seldom been documented. In this study, molecular analysis was performed on Anisakis larvae from the sea eels (Astroconger myriaster), the major source of human anisakiasis in Korea, collected from Tongyeong City, a southern coastal area of Korea. All 20 sea eels examined were infected with Anisakis type I larvae (160 larvae; 8 per fish). Their species were analyzed using PCR-RFLP patterns and nucleotide sequences of internal transcribed spacers (ITS1, 5.8 subunit gene, and ITS2) and mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase 2 (cox2). Most (86.8%; 112/129) of the Anisakis type I larvae were A. pegreffii, and 7.8% (10/129) were A. typica. The remaining 5.4% (7/129) was not identified. Thus, A. pegreffii is the major species of anisakid larvae in sea eels of the southern coast of Korea.
Keywords: Anisakis pegreffii; ITS1; PCR-RFLP; cox2; sea eel.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Identification of Anisakis Larvae Extracted by Gastrointestinal Endoscopy from Health Check-up Patients in Korea.Korean J Parasitol. 2019 Apr;57(2):207-211. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.2.207. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Korean J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31104416 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of Anisakis species (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from marine fishes collected in Turkish waters.Vet Parasitol. 2014 Mar 17;201(1-2):82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Vet Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24485564
-
Molecular analysis of Anisakis type I larvae in marine fish from three different sea areas in Korea.Korean J Parasitol. 2014 Aug;52(4):383-9. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2014.52.4.383. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Korean J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25246717 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating animal health surveillance and food safety: the example of Anisakis.Rev Sci Tech. 2013 Aug;32(2):487-96. doi: 10.20506/rst.32.2.2246. Rev Sci Tech. 2013. PMID: 24547652 Review.
-
Reviewing biodiversity and epidemiological aspects of anisakid nematodes from the North-east Atlantic Ocean.J Helminthol. 2017 Jul;91(4):422-439. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X1700027X. Epub 2017 Apr 11. J Helminthol. 2017. PMID: 28397641 Review.
Cited by
-
Anisakiasis Causing Acute Dysentery in Malaysia.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016 Aug 3;95(2):410-2. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0007. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016. PMID: 27325803 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Anisakid Nematodes in Fish in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 21;9:792346. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.792346. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35265693 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analyses of Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from the East Asian finless porpoise Neophocaena asiaeorientalis sunameri (Cetacea: Phocoenidae) in Korean waters.Parasitol Res. 2024 Oct 31;123(11):365. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08368-x. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39477870 Free PMC article.
-
Anisakidae and Anisakidosis: A Public Health Perspective.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 22;14(3):217. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030217. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40137702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First morphological and molecular identification of third-stage larvae of Anisakis typica (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from marine fishes in Vietnamese water.J Nematol. 2021 Feb 19;53:e2021-10. doi: 10.21307/jofnem-2021-010. eCollection 2021. J Nematol. 2021. PMID: 33860256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sohn WM, Chai JY. Anisakiosis (Anisakidosis) In: Palmer SR, Soulsby L, Torgerson PR, Brown WG, editors. Oxford Textbook of Zoonoses. 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2011. pp. 774–786.
-
- Chai JY, Murrell KD, Lymbery AJ. Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: status and issues. Int J Parasitol. 2005;35:1233–1254. - PubMed
-
- D’Amelio S, Mathiopoulos KD, Brandonisio O, Lucarelli G, Doron zo F, Paggi L. Diagnosis of a case of gastric anisakidosis by PCR-based restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Parassitologia. 1999;41:591–593. - PubMed
-
- Fumarola L, Monno R, Ierardi E, Rizzo G, Giannelli G, Lalle M, Pozio E. Anisakis pegreffii etiological agent of gastric infections in two Italian women. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009;6:1157–1159. - PubMed
-
- Mattiucci S, Paoletti M, Borrini F, Palumbo M, Palmieri RM, Gomes V, Casati A, Nascetti G. First molecular identification of the zoonotic parasite Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in a paraffin-embedded granuloma taken from a case of human intestinal anisakiasis in Italy. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11(1-6):82. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

