Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics of Prostate Tuberculosis
- PMID: 26175584
- PMCID: PMC4499549
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.846
Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics of Prostate Tuberculosis
Abstract
Objective: To describe the multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance of prostate tuberculosis.
Materials and methods: Six patients with prostate tuberculosis were analyzed retrospectively. The mean age of the patients was 60.5 years (range, 48-67 years). The mean prostate specific antigen concentration was 6.62 ng/mL (range, 0.54-14.57 ng/mL). All patients underwent a multiparametric MRI examination.
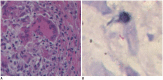
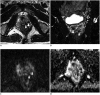
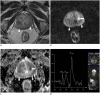
Results: The histopathological results were obtained from biopsies in four men and from transurethral resection of the prostate in two men after the MRI examination. Nodular (33%, 2/6 patients) and diffuse lesions (67%, 4/6 patients) were seen on MRI. The nodular lesions were featured by extremely low signal intensity (similar to that of muscle) on T2-weighted imaging (T2WI). The T2WI signal intensity of the diffuse lesions was low but higher than that of muscle, which showed high signal intensity on diffusion weighted imaging and low signal intensity on an apparent diffusion coefficient map. MR spectroscopic imaging of this type showed a normal-like spectrum. Abscesses were found in one patient with the nodular type and in one with the diffuse type.
Conclusion: The appearance of prostate tuberculosis on MRI can be separated into multiple nodular and diffuse types. Multiparametric MRI may offer useful information for diagnosing prostate tuberculosis.
Keywords: Diffuse; MRI; Multiple nodular; Prostate tuberculosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MRI findings of granulomatous prostatitis developing after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy.Clin Radiol. 2013 Jun;68(6):595-9. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Clin Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23384503
-
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of chronic prostatitis in patients under the age of 50: is it more than the eye can see?Acta Radiol. 2022 Jun;63(6):839-846. doi: 10.1177/02841851211010397. Epub 2021 May 3. Acta Radiol. 2022. PMID: 33940959
-
Abbreviated Biparametric Prostate MR Imaging in Men with Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen.Radiology. 2017 Nov;285(2):493-505. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017170129. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Radiology. 2017. PMID: 28727544
-
Multiparametric MRI in detection and staging of prostate cancer.Dan Med J. 2017 Feb;64(2):B5327. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28157066 Review.
-
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of prostate cancer.Aktuelle Urol. 2014 Mar;45(2):119-26. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1371875. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Aktuelle Urol. 2014. PMID: 24700068 Review.
Cited by
-
BCG instillations can mimic prostate cancer on multiparametric MRI.Int Braz J Urol. 2018 Jul-Aug;44(4):835-837. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0621. Int Braz J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29570255 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Imaging findings of prostate tuberculosis by transrectal contrast-enhanced ultrasound and comparison with 2D ultrasound and pathology.Br J Radiol. 2022 Jan 1;95(1129):20210713. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210713. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34586884 Free PMC article.
-
Genitourinary Tuberculosis: A Comprehensive Review of a Neglected Manifestation in Low-Endemic Countries.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;10(11):1399. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111399. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computed tomography imaging analysis of hematogenous disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis cases combined with prostate tuberculosis.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01753-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40597764 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the deceiver: the non-neoplastic mimickers of genital system neoplasms.Insights Imaging. 2021 Jul 7;12(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-01046-x. Insights Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34232414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen Y, Liu M, Guo Y. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in prostate tuberculosis. Urology. 2010;75:1065–1066. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Takeuchi M, Naiki T, Kawai N, Kohri K, Hara M, et al. MRI findings of granulomatous prostatitis developing after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy. Clin Radiol. 2013;68:595–599. - PubMed
-
- Ma W, Kang SK, Hricak H, Gerst SR, Zhang J. Imaging appearance of granulomatous disease after intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) treatment of bladder carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192:1494–1500. - PubMed
-
- Bour L, Schull A, Delongchamps NB, Beuvon F, Muradyan N, Legmann P, et al. Multiparametric MRI features of granulomatous prostatitis and tubercular prostate abscess. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94:84–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

