PubChemRDF: towards the semantic annotation of PubChem compound and substance databases
- PMID: 26175801
- PMCID: PMC4500850
- DOI: 10.1186/s13321-015-0084-4
PubChemRDF: towards the semantic annotation of PubChem compound and substance databases
Abstract
Background: PubChem is an open repository for chemical structures, biological activities and biomedical annotations. Semantic Web technologies are emerging as an increasingly important approach to distribute and integrate scientific data. Exposing PubChem data to Semantic Web services may help enable automated data integration and management, as well as facilitate interoperable web applications.
Description: This work, one of a series covering the PubChemRDF project, describes an approach to translate PubChem Substance and Compound information into Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. Basic examples are provided to demonstrate its use. The aim of this effort is to provide two new primary benefits to researchers in a cost-effective manner. Firstly, we aim to remove the inherent limitations of using the web-based resource PubChem by allowing a researcher to use readily available semantic technologies (namely, RDF triple stores and their corresponding SPARQL query engines) to query and analyze PubChem data on local computing resources. Secondly, this work intends to help improve data sharing, analysis, and integration of PubChem data to resources external to NCBI and across scientific domains, by means of the association of PubChem data to existing ontological frameworks, including CHEMical INFormation ontology, Semanticscience Integrated Ontology, and others.
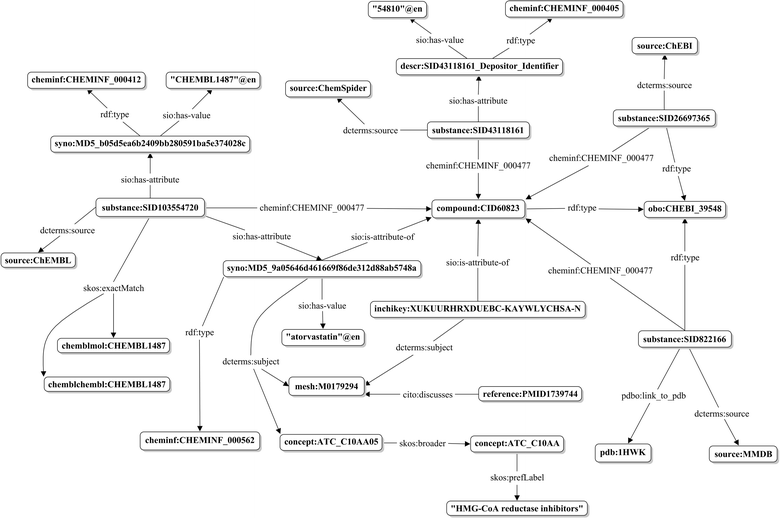
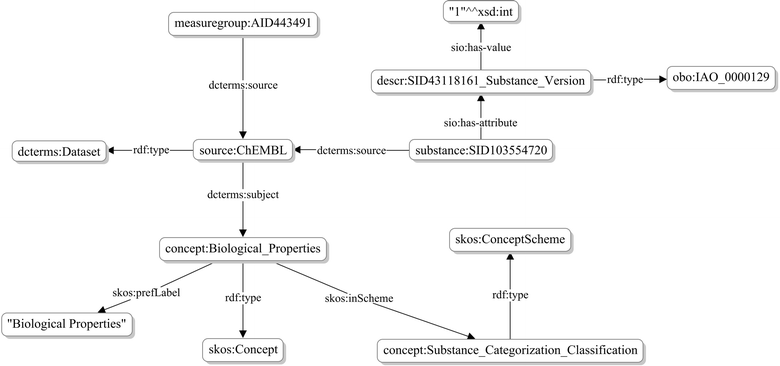
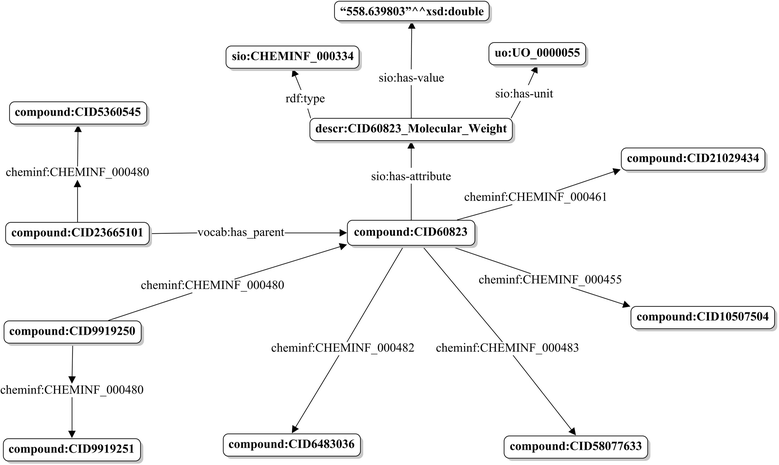
Conclusions: With the goal of semantically describing information available in the PubChem archive, pre-existing ontological frameworks were used, rather than creating new ones. Semantic relationships between compounds and substances, chemical descriptors associated with compounds and substances, interrelationships between chemicals, as well as provenance and attribute metadata of substances are described. Graphical abstract:Schematic representation of the semantic links for PubChem compounds and substances.
Figures


References
-
- PubChem. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Accessed 8 July 2015
-
- Bolton EE, Wang Y, Thiessen PA, Bryant SH (2008) Chapter 12 PubChem: integrated platform of small molecules and biological activities. In: Ralph AW, David CS (eds) Annual reports in computational chemistry, vol 4. Elsevier, USA, pp 217–241
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

