Effect of NaCl Addition on Rheological Behaviors of Commercial Gum-Based Food Thickener Used for Dysphagia Diets
- PMID: 26176002
- PMCID: PMC4500517
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2015.20.2.137
Effect of NaCl Addition on Rheological Behaviors of Commercial Gum-Based Food Thickener Used for Dysphagia Diets
Abstract
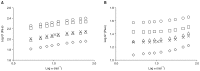
Rheological properties of thickened fluids used for consumption by people with dysphagia (swallowing difficulty) are very sensitive to several factors, such as thickener type, temperature, pH, sugar, protein, and NaCl. In this study, steady and dynamic rheological properties of thickened water samples mixed with five commercial xanthan gum-based food thickeners (A~E) were studied in the presence of NaCl at different concentrations (0.3%, 0.6%, 0.9%, and 1.2%). The magnitudes of apparent viscosity (ηa,50), consistency index (K), yield stress (σoc), and dynamic moduli (G' and G″) showed significant differences in rheological behaviors between thickened samples with various NaCl concentrations. Dynamic moduli values of all thickened samples, except for samples with thickener C, were much higher than those of the control (0% NaCl). All rheological parameter values (K, G', and G″) in a thickener A were much higher than those in other thickeners. These results suggest that rheological properties of thickened samples containing NaCl are strongly affected by xanthan gum-NaCl interaction and depended on the type of thickener.
Keywords: NaCl; food thickener; rheological property; viscosity; xanthan gum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rheological characteristics of cold thickened beverages containing xanthan gum-based food thickeners used for dysphagia diets.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Jan;115(1):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2014.08.028. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015. PMID: 25441963
-
Effect of thickener type on the rheological properties of hot thickened soups suitable for elderly people with swallowing difficulty.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2014 Dec;19(4):358-62. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2014.19.4.358. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2014. PMID: 25580403 Free PMC article.
-
Rheological characterization of thickened protein-based beverages under different food thickeners and setting times.J Texture Stud. 2018 Jun;49(3):293-299. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12332. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Texture Stud. 2018. PMID: 29574854
-
Influence of thickening agents on rheological properties and sensory attributes of dysphagic diet.J Texture Stud. 2021 Dec;52(5-6):587-602. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12596. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Texture Stud. 2021. PMID: 33760237 Review.
-
Food polysaccharides and roles of rheology and tribology in rational design of thickened liquids for oropharyngeal dysphagia: A review.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021 Jul;20(4):4101-4119. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12791. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021. PMID: 34146451 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Texture Modified Foods for Oro-pharyngeal Dysphagia: A Difficult but Possible Target?Front Nutr. 2018 Aug 7;5:68. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00068. eCollection 2018. Front Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30131962 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Food and Liquid Properties on Swallowing Physiology and Function in Adults.Dysphagia. 2023 Jun;38(3):785-817. doi: 10.1007/s00455-022-10525-2. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Dysphagia. 2023. PMID: 36266521 Review.
-
A Thickening Agent Using Dioscorea japonica Powder Exhibits Suitable Properties for People with Dysphagia.Foods. 2023 Oct 28;12(21):3943. doi: 10.3390/foods12213943. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanek K, Hensley C, Van Riper C. Factors affecting use of food and commercial agents to thicken liquids for individuals with swallowing disorders. J Am Diet Assoc. 1992;92:488–490. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources