Translational readthrough potential of natural termination codons in eucaryotes--The impact of RNA sequence
- PMID: 26176195
- PMCID: PMC4615788
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1068497
Translational readthrough potential of natural termination codons in eucaryotes--The impact of RNA sequence
Abstract
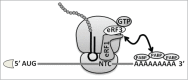
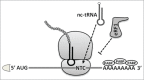
Termination of protein synthesis is not 100% efficient. A number of natural mechanisms that suppress translation termination exist. One of them is STOP codon readthrough, the process that enables the ribosome to pass through the termination codon in mRNA and continue translation to the next STOP codon in the same reading frame. The efficiency of translational readthrough depends on a variety of factors, including the identity of the termination codon, the surrounding mRNA sequence context, and the presence of stimulating compounds. Understanding the interplay between these factors provides the necessary background for the efficient application of the STOP codon suppression approach in the therapy of diseases caused by the presence of premature termination codons.
Keywords: STOP codon suppression; mRNA; near-cognate tRNA; premature termination codon; termination codon; translational readthrough.
Figures
References
-
- Dever TE, Green R. The elongation, termination, and recycling phases of translation in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012; 4:a013706; PMID:22751155; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a013706 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scolnick E, Tompkins R, Caskey T, Nirenberg M. Release factors differing in specificity for terminator codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1968; 61:768-74; PMID:4879404; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.61.2.768 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Ito K. A tripeptide discriminator for stop codon recognition. FEBS Lett 2002; 514:30-3; PMID:11904176; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02330-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zavialov AV, Buckingham RH, Ehrenberg M. A posttermination ribosomal complex is the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for peptide release factor RF3. Cell 2001; 107:115-24; PMID:11595190; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00508-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alkalaeva EZ, Pisarev AV, Frolova LY, Kisselev LL, Pestova TV. In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell 2006; 125:1125-36; PMID:16777602; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.035 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
