Integrin-linked kinase regulates senescence in an Rb-dependent manner in cancer cell lines
- PMID: 26176204
- PMCID: PMC4825635
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1064205
Integrin-linked kinase regulates senescence in an Rb-dependent manner in cancer cell lines
Abstract
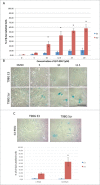
Anti-integrin-linked kinase (ILK) therapies result in aberrant mitosis including altered mitotic spindle organization, centrosome declustering and mitotic arrest. In contrast to cells that expressed the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein Rb, we have shown that in retinoblastoma cell lines that do not express Rb, anti-ILK therapies induced aberrant mitosis that led to the accumulation of temporarily viable multinucleated cells. The present work was undertaken to: 1) determine the ultimate fate of cells that had survived anti-ILK therapies and 2) determine whether or not Rb expression altered the outcome of these cells. Our data indicate that ILK, a chemotherapy drug target is expressed in both well-differentiated, Rb-negative and relatively undifferentiated, Rb-positive retinoblastoma tissue. We show that small molecule targeting of ILK in Rb-positive and Rb-deficient cancer cells results in increased centrosomal declustering, aberrant mitotic spindle formation and multinucleation. However, anti-ILK therapies in vitro have different outcomes in retinoblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines that depend on Rb expression. TUNEL labeling and propidium iodide FACS analysis indicate that Rb-positive cells exposed to anti-ILK therapies are more susceptible to apoptosis and senescence than their Rb-deficient counterparts wherein aberrant mitosis induced by anti-ILK therapies exhibit mitotic arrest instead. These studies are the first to show a role for ILK in chemotherapy-induced senescence in Rb-positive cancer lines. Taken together these results indicate that the oncosuppressive outcomes for anti-ILK therapies in vitro, depend on the expression of the tumor suppressor Rb, a known G1 checkpoint and senescence regulator.
Keywords: Integrin-linked kinase; cancer; centrosome declustering; mitotic arrest; multinucleation; multipolar mitosis; retinoblastoma; senescence.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Regulation of mitotic cytoskeleton dynamics and cytokinesis by integrin-linked kinase in retinoblastoma cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 9;9(6):e98838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098838. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24911651 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role of integrin-linked kinase, ch-TOG and TACC3 in centrosome clustering in cancer cells.Oncogene. 2011 Feb 3;30(5):521-34. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.431. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 20838383
-
Combination Effects of Integrin-linked Kinase and Abelson Kinase Inhibition on Aberrant Mitosis and Cell Death in Glioblastoma Cells.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;12(7):906. doi: 10.3390/biology12070906. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508338 Free PMC article.
-
The mitotic functions of integrin-linked kinase.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):99-111. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9177-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009. PMID: 19153670 Review.
-
Integrin-linked kinase: A new actor in the ageing process?Exp Gerontol. 2017 Dec 15;100:87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.10.026. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 29101014 Review.
Cited by
-
Bufalin enhances antitumor effect of paclitaxel on cervical tumorigenesis via inhibiting the integrin α2/β5/FAK signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):8896-907. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6840. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26758421 Free PMC article.
-
The kinase activity of integrin-linked kinase regulates cellular senescence in gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jul 1;13(7):577. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05020-3. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35778385 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profile and Function Analysis of LncRNAs during Priming Phase of Rat Liver Regeneration.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 21;11(6):e0156128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156128. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27326854 Free PMC article.
-
Bufalin inhibits glycolysis-induced cell growth and proliferation through the suppression of Integrin β2/FAK signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 1;8(7):1288-1296. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30094101 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Role for Integrin-Linked Kinase in Colorectal Cancer Growth and Progression via Regulating Senescence and Immunity.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 7;12:638558. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.638558. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34163519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fielding AB, Lim S, Montgomery K, Dobreva I, Dedhar S. A critical role of integrin-linked kinase, ch-TOG and TACC3 in centrosome clustering in cancer cells. Oncogene 2011; 30:521-34; PMID:20838383; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.431 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fielding AB, Dobreva I, McDonald PC, Foster LJ, Dedhar S. Integrin-linked kinase localizes to the centrosome and regulates mitotic spindle organization. J Cell Biol 2008; 180:681-9; PMID:18283114; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200710074 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fielding AB, Dobreva I, Dedhar S. Beyond focal adhesions: integrin-linked kinase associates with tubulin and regulates mitotic spindle organization. Cell Cycle 2008; 7:1899-906; PMID:18604167; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.13.6204 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lim S, Kawamura E, Fielding AB, Maydan M, Dedhar S. Integrin-linked kinase regulates interphase and mitotic microtubule dynamics. PloS one 2013; 8:e53702; PMID:23349730; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053702 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
