Short- versus Long-Sarafotoxins: Two Structurally Related Snake Toxins with Very Different in vivo Haemodynamic Effects
- PMID: 26176218
- PMCID: PMC4503772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132864
Short- versus Long-Sarafotoxins: Two Structurally Related Snake Toxins with Very Different in vivo Haemodynamic Effects
Abstract
Sarafotoxin-m (24 amino acids) from the venom of Atractaspis microlepidota microlepidota was the first long-sarafotoxin to be identified, while sarafotoxin-b (21 aa) is a short-sarafotoxin from Atractaspis engaddensis. Despite the presence of three additional C-terminus residues in sarafotoxin-m, these two peptides display a high sequence homology and share similar three-dimensional structures. However, unlike sarafotoxin-b, sarafotoxin-m shows a very low in vitro affinity for endothelin receptors, but still has a very high in vivo toxicity in mammals, similar to that of sarafotoxin-b. We have previously demonstrated, in vitro, the crucial role of the C-terminus extension in terms of pharmacological profiles and receptor affinities of long- versus short-sarafotoxins. One possible hypothesis to explain the high in vivo toxicity of sarafotoxin-m could be that its C-terminus extension is processed in vivo, resulting in short-like sarafotoxin. To address this possibility, we investigated, in the present study, the in vivo cardiovascular effects of sarafotoxin-b, sarafotoxin-m and sarafotoxin-m-Cter (sarafotoxin-m without the C -terminus extension). Male Wistar rats were anaesthetised and mechanically ventilated. Invasive haemodynamic measurements and echocardiographic measurements of left and right ventricular function were performed. The rats were divided into four groups that respectively received intravenous injections of: saline, sarafotoxin-b (one LD50), sarafotoxin-m (one LD50) or sarafotoxin-m-Cter (one LD50). All measurements were performed at baseline, at 1 minute (+1) and at 6 minutes (+6) after injection.
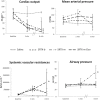
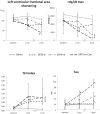
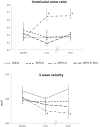
Results: Sarafotoxin-b and sarafotoxin-m-Cter decreased cardiac output and impaired left ventricle systolic and diastolic function, whilst sarafotoxin-m decreased cardiac output, increased airway pressures and led to acute right ventricular dilatation associated with a decreased tricuspid annulus peak systolic velocity. Sarafotoxin-b and sarafotoxin-m-Cter appear to exert toxic effects via impairment of left ventricular function, whilst sarafotoxin-m increases airway pressures and impairs right ventricular function. These results do not support the hypothesis of an in vivo processing of long sarafotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Acute Cardiovascular Effects of an Endothelin-Like Peptide Extracted from the Venom of Atractaspis irregularis.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017 Apr;17(2):208-214. doi: 10.1007/s12012-016-9376-9. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27358047
-
Respiratory Effects of Sarafotoxins from the Venom of Different Atractaspis Genus Snake Species.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 11;8(7):215. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070215. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27409637 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and structural characterization of long-sarafotoxins, a new family of endothelin-like peptides: Role of the C-terminus extension.Biochimie. 2012 Feb;94(2):461-70. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.08.014. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 21889567
-
Sarafotoxins and endothelins: evolution, structure and function.Toxicon. 1993 May;31(5):541-68. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(93)90111-u. Toxicon. 1993. PMID: 8332988 Review.
-
Endothelins and sarafotoxins: peptides of similar structure and different function.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2004;47(3):157-62. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2004. PMID: 15568731 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Functional Diversity of Animal Toxins Interacting With GPCRs.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 7;9:811365. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.811365. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35198603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Effects of Snake Toxins: Cardiotoxicity and Cardioprotection.Acta Naturae. 2021 Jul-Sep;13(3):4-14. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11375. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 34707893 Free PMC article.
-
Toxinology provides multidirectional and multidimensional opportunities: A personal perspective.Toxicon X. 2020 May 11;6:100039. doi: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2020.100039. eCollection 2020 Jun. Toxicon X. 2020. PMID: 32550594 Free PMC article.
-
Snake Venom Components as Therapeutic Drugs in Ischemic Heart Disease.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 18;13(10):1539. doi: 10.3390/biom13101539. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Snake Venom Peptides: Tools of Biodiscovery.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 14;10(11):474. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110474. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30441876 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988;332: 411–415. - PubMed
-
- Wollberg Z, Shabo-Shina R, Intrator N, Bdolah A, Kochva E, Shavit G, et al. A novel cardiotoxic polypeptide from the venom of Atractaspis engaddensis (burrowing asp): cardiac effects in mice and isolated rat and human heart preparations. Toxicon. 1988;26: 525–534. - PubMed
-
- Sokolovsky M. Endothelins and sarafotoxins: physiological regulation, receptor subtypes and transmembrane signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991;16: 261–264. - PubMed
-
- Ducancel F. The sarafotoxins. Toxicon. 2002;40: 1541–1545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

