Adding Hydrochlorothiazide to Olmesartan/Amlodipine Increases Efficacy in Patients With Inadequate Blood Pressure Control on Dual-Combination Therapy
- PMID: 26176708
- PMCID: PMC5034748
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12621
Adding Hydrochlorothiazide to Olmesartan/Amlodipine Increases Efficacy in Patients With Inadequate Blood Pressure Control on Dual-Combination Therapy
Abstract
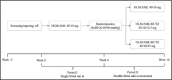
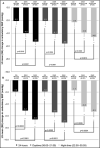
This randomized, parallel-group study in patients inadequately controlled on olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine (OLM/AML) 40/10 mg assessed the effects of adding hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 12.5 mg and 25 mg, using seated blood pressure (SeBP) measurements and ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring. Enrolled patients were screened and tapered off of therapy if required. All patients received OLM/AML 40/10 mg and those with mean seated BP (SeBP) ≥140/90 mm Hg after 8 weeks (n=808) were randomized (1:1:1) to continue with OLM/AML 40/10 mg or receive OLM/AML/HCTZ 40/10/12.5 or 40/10/25 mg for a further 8 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in seated diastolic BP (SeDBP) from the start to the end of the randomized treatment period. The addition of HCTZ 25 mg significantly reduced SeDBP (-2.8 mm Hg; P<.0001), lowered seated systolic BP (SeSBP) and ambulatory DBP and SBP, and improved BP goal rates. In patients uncontrolled on OLM/AML 40/10 mg, adding HCTZ led to further BP reductions, particularly in ambulatory BP.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triple therapy with olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine besylate, and hydrochlorothiazide in adult patients with hypertension: The TRINITY multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 12-week, parallel-group study.Clin Ther. 2010 Jul;32(7):1252-69. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.07.008. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20678674 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of olmesartan medoxomil 40 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg combination therapy versus olmesartan medoxomil 40 mg monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational, phase III study.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(9):581-97. doi: 10.2165/11536710-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20593911 Clinical Trial.
-
The combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine besylate in controlling high blood pressure: COACH, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 8-week factorial efficacy and safety study.Clin Ther. 2008 Apr;30(4):587-604. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.04.002. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18498909 Clinical Trial.
-
Olmesartan medoxomil combined with hydrochlorothiazide for the treatment of hypertension.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2(4):401-9. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.4.401. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006. PMID: 17323594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood pressure control with angiotensin receptor blocker-based three-drug combinations: key trials.Adv Ther. 2012 May;29(5):401-15. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0019-7. Epub 2012 May 17. Adv Ther. 2012. PMID: 22610686 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of olmesartan medoxomil-amlodipine besylate tablet in Chinese patients with essential hypertension: A prospective, single-arm, multi-center, real-world study.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 Jan;26(1):5-16. doi: 10.1111/jch.14700. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 37667532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–1357. - PubMed
-
- Jamerson K, Weber MA, Bakris GL, et al. Benazepril plus amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high‐risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2417–2428. - PubMed
-
- Pepine CJ, Handberg EM, Cooper‐DeHoff RM, et al. A calcium antagonist vs a non‐calcium antagonist hypertension treatment strategy for patients with coronary artery disease. The International Verapamil‐Trandolapril Study (INVEST): a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2805–2816. - PubMed
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, et al. Effects of intensive blood‐pressure lowering and low‐dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. HOT Study Group. Lancet. 1998;351:1755–1762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

