Microarray Analysis Reveals Potential Biological Functions of Histone H2B Monoubiquitination
- PMID: 26177367
- PMCID: PMC4503354
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133444
Microarray Analysis Reveals Potential Biological Functions of Histone H2B Monoubiquitination
Abstract
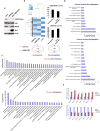
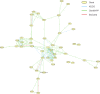
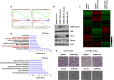
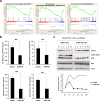
Histone H2B monoubiquitination is a key histone modification that has significant effects on chromatin higher-order structure and gene transcription. Multiple biological processes have been suggested to be tightly related to the dynamics of H2B monoubiquitination. However, a comprehensive understanding of biological roles of H2B monoubiquitination is still poorly understood. In the present study, we developed an efficient tool to disrupt endogenous H2B monoubiquitination levels by using an H2BK120R mutant construct expressed in human cells. Genome-wide microarray analysis of these cells revealed a potential global view of biological functions of H2B monoubiquitination. Bioinformatics analysis of our data demonstrated that while H2B monoubiquitination expectedly affected a number of previously reported biological pathways, we also uncovered the influence of this histone modification on many novel biological processes. Therefore, our work provided valuable information for understanding the role of H2B monoubiquitination and indicated potential directions for its further studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

