No Added Value of Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Assessment of Patients Suspected of Acute Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 26177390
- PMCID: PMC4503345
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132000
No Added Value of Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnostic Assessment of Patients Suspected of Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Despite the availability of high-sensitive troponin (hs-cTnT), there is still room for improvement in the diagnostic assessment of patients suspected of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Apart from serial biomarker testing, which is time-consuming, novel biomarkers like copeptin have been proposed to expedite the early diagnosis of suspected ACS in addition to hs-cTnT. We determined whether placenta derived growth factor (PlGF), soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1), myoglobin, N-terminal prohormone B-type Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP), growth-differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) and copeptin improved early assessment of chest pain patients.
Methods: This prospective, single centre diagnostic FAME-ER study included patients presenting to the ED with symptoms suggestive of ACS. Blood was collected to measure biomarkers, notably, hs-cTnT was retrospectively assessed. Added value of markers was judged by increase in AUC using multivariable logistic regression.
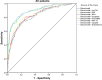
Results: Of 453 patients enrolled, 149 (33%) received a final diagnosis of ACS. Hs-cTnT had the highest diagnostic value in both univariable and multivariable analysis. PPVs of the biomarkers ranged from 23.5% (PlGF) to 77.9% (hs-cTnT), NPVs from 67.0% (PlGF) to 86.4% (hs-cTnT). Only myoglobin yielded diagnostic value in addition to clinical symptoms and electrocardiography (ECG) (AUC of clinical model 0.80) with AUC of 0.84 (p<0.001). However, addition of hs-cTnT was superior (AUC 0.89, p<0.001). Addition of the biomarkers to our clinical model and hs-cTnT did not or only marginally (GDF-15) improved diagnostic performance.
Conclusion: When assessing patients suspected of ACS, only myoglobin had added diagnostic value beyond clinical symptoms and ECG. However, when combined with hs-cTnT, it yields no additional diagnostic value. PlGF, sFlt-1, NT-proBNP, GDF-15 and copeptin had no added value to the clinical model or hs-cTnT.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bassand JP, Hamm CW, Ardissino D, Boersma E, Budaj A, Fernández-Avilés F, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2007;28(13):1598–1660. - PubMed
-
- Hamm CW1, Bassand JP, Agewall S, Bax J, Boersma E, Bueno H, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2011. December;32(23):2999–3054. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr236 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation 2007;116(22):2634–2653. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

