EphA2 Is a Potential Player of Malignant Cellular Behavior in Non-Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells but Not in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 26177500
- PMCID: PMC4503437
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130975
EphA2 Is a Potential Player of Malignant Cellular Behavior in Non-Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells but Not in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the role of EphA2 in malignant cellular behavior in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells and whether FAK/RhoA signaling can act as downstream effectors of EphA2 on RCC cells.
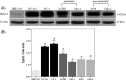
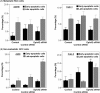
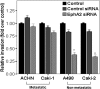
Methods: Expression of EphA2 protein in non-metastatic RCC (Caki-2 and A498), metastatic RCC cells (Caki-1 and ACHN), HEK-293 cells and prostate cancer cells (PC-3 and DU-145; positive controls of EphA2 expression) was evaluated by Western blot. Changes in mRNA or protein expression of EphA2, FAK or membrane-bound RhoA following EphA2, FAK or RhoA small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection were determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction or Western blot. The effect of siRNA treatment on cellular viability, apoptosis and invasion was analyzed by cell counting kit-8, Annexin-V and modified Matrigel-Boyden assays, respectively.
Results: In all RCC cell lines, the expression of EphA2 protein was detectable at variable levels; however, in HEK-293 cells, EphA2 expression was very low. Treatment with EphA2 siRNA significantly reduced the expression of EphA2 mRNA and protein in all RCC cell lines. For non-metastatic RCC cells (Caki-2 and A498) but not metastatic RCC cells (Caki-1 and ACHN), cellular viability, invasiveness, resistance to apoptosis, expression of membrane-bound RhoA protein and FAK phosphorylation were significantly decreased in EphA2 siRNA-treated cells compared to the control. In non-metastatic RCC cells, FAK siRNA significantly attenuated the invasiveness, resistance to apoptosis, as well as expression of membrane-bound RhoA protein without changing protein expression of EphA2. RhoA siRNA significantly decreased the malignant cellular behavior and expression of membrane-bound RhoA protein without changing EphA2 protein expression or FAK phosphorylation.
Conclusions: Our data provide the first functional evidence that the EphA2/FAK/RhoA signaling pathway plays a critical role in the malignant cellular behavior of RCC and appears to be functional particularly in the early stage of malignant progression of non-metastatic RCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Silencing of lysyl oxidase‑like 2 inhibits the migration, invasion and epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells through the Src/FAK signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2019 May;54(5):1676-1690. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4726. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30816490 Free PMC article.
-
miR-141 is a key regulator of renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by controlling EphA2 expression.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 May 15;20(10):2617-30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3224. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24647573
-
Hypoxia-induced overexpression of stanniocalcin-1 is associated with the metastasis of early stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2015 Feb 12;13:56. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0421-4. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25740019 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression and functional alterations of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase in cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20(1):59-68. doi: 10.1023/a:1022546620495. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003. PMID: 12650608 Review.
-
EphA2-dependent molecular targeting therapy for malignant tumors.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011 Nov;11(9):1082-97. doi: 10.2174/156800911798073050. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21933105 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Nuclear Claudin-4 in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 6;21(21):8340. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218340. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33172177 Free PMC article.
-
Development of EphA2 siRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles and combination with a small-molecule histone demethylase inhibitor in prostate cancer cells and tumor spheroids.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Mar 8;19(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00781-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33685469 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Physical Forces Experienced by Cancer and Stromal Cells Within Different Organ-Specific Tumor Tissue.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2024 Apr 15;12:413-434. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2024.3388561. eCollection 2024. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38765886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cindolo L, Patard JJ, Chiodini P, Schips L, Ficarra V, Tostain J, et al. (2005) Comparison of predictive accuracy of four prognostic models for nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy: A multicenter European study. Cancer 104: 1362–1371. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B (2009) Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 28: 1119–1132. - PubMed
-
- Castaño J, Davalos V, Schwartz S Jr, Arango D (2008) EPH receptors in cancer. Histol Histopathol 23: 1011–1023. - PubMed
-
- Ireton RC, Chen J (2005) EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5: 149–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

