Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents TCDD-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response by modulating MAP kinases and redox-sensitive transcription factors
- PMID: 26177858
- PMCID: PMC4594275
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13247
Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents TCDD-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response by modulating MAP kinases and redox-sensitive transcription factors
Abstract
Background and purpose: Oxidative stress and subsequent activation of inflammatory responses is a widely accepted consequence of exposure to environmental toxins. TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin), a well-known environmental toxin, exerts its toxicity through many signalling mechanisms, with liver being the principal organ affected. However, an effective antidote to TCDD-induced toxicity is unknown. The present study evaluated the effect of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), an n3 fatty acid, on TCDD-induced toxicity.
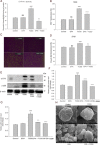
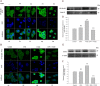
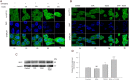
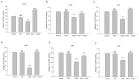
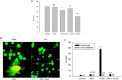
Experimental approach: In cultures of HepG2 cells, the EPA/AA ratio was determined using gas chromatography, oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, antioxidant status, [Ca(2+) ]i , nuclear migration of two redox-sensitive transcription factors, NF-κB p65 and Nrf-2, expression of MAP kinase (p-Erk, p-p38), NF-κB p65, COX-2 and Nrf-2. Cellular changes in ΔΨm, acidic vesicular organelle formation, cell cycle analysis and scanning electron microscopy analysis were performed.
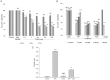
Key results: EPA offered significant cytoprotection by increasing EPA/AA ratios in cell membranes, inhibiting ROS generation, enhancing antioxidant status and modulating nuclear translocation of redox-sensitive transcription factors (NF-κB p65 and Nrf-2) and expression of NF-κB p65, COX-2 and Nrf-2. Furthermore, TCDD-induced upstream events of MAPK phosphorylation, the increase in [Ca(2+) ]i levels and cell surface changes in microvilli were significantly inhibited by EPA. EPA treatment maintained ΔΨm and prevented formation of acidic vesicular organelles.
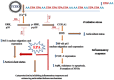
Conclusion and implications: The present study demonstrates for the first time some underlying molecular mechanisms of cytoprotection exerted by EPA against TCDD-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quercetin modulates OTA-induced oxidative stress and redox signalling in HepG2 cells - up regulation of Nrf2 expression and down regulation of NF-κB and COX-2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1840(1):681-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24161694
-
Fish oil rich in eicosapentaenoic acid protects against oxidative stress-related renal dysfunction induced by TCDD in Wistar rats.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014 May;19(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s12192-013-0470-7. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014. PMID: 24114387 Free PMC article.
-
Actein alleviates 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-mediated cellular dysfunction in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Dec;32(12):2455-2470. doi: 10.1002/tox.22459. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28836330
-
ROS and RNS signalling: adaptive redox switches through oxidative/nitrosative protein modifications.Free Radic Res. 2018 May;52(5):507-543. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2018.1457217. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Free Radic Res. 2018. PMID: 29589770 Review.
-
Oxidative stress induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD).Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;9(1):79-90. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90052-k. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990. PMID: 2210442 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Profiling of Oxylipin Reveals the Mechanism of Pien-Tze-Huang on Alcoholic Liver Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 1;2021:9931542. doi: 10.1155/2021/9931542. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34158817 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Modulates the Expression of TNF-α and IL-8 in Human Sebocytes via the MyD88-p65NF-κB/p38MAPK Signaling Pathways.J Innate Immun. 2019;11(1):41-51. doi: 10.1159/000491029. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 30056444 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2017 Dec;4(4):439-449. doi: 10.1007/s40572-017-0166-8. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2017. PMID: 28980219 Review.
-
The antioxidant and therapeutic effects of Malva sylvestris extract on testicular tissue and sperm quality in varicocele-induced adult Wistar rats.Basic Clin Androl. 2025 Jun 16;35(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12610-025-00271-4. Basic Clin Androl. 2025. PMID: 40524181 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipids Mediators on Cardiac Fibrosis via NRF2 Activation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 10;9(12):1259. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121259. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33321955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase. In: Bergmeyer H, editor. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. New York: Academic Press; 1974. pp. 673–684.
-
- Azad MB, Chen Y, Gibson SB. Regulation of autophagy by reactive oxygen species (ROS): implications for cancer progression and treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:777–790. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

