The Diagnosis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 26179016
- PMCID: PMC4558874
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2015.0423
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
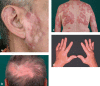
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with a prevalence of 36.7/100 000 in Germany and a female/male ratio of 4:1. The clinical course is variable, with a broad spectrum of organ manifestations; lupus nephritis develops in about half of all patients.
Methods: This review is based on a selective search of PubMed and the Cochrane Library, including current guidelines and expert recommendations.
Results: Assessment of clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, and optional biopsy results are the basis for early diagnosis of SLE. All patients should be treated with antimalarials as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. In particular, hydroxychloroquine is associated with a higher rate of remission, fewer relapses, and reduced damage in the course of the disease, even in lupus nephritis. High-dose glucocorticoids should be given only when acutely indicated; immunosuppressives such as azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil may be administered to reduce glucocorticoids, according to the EULAR recommendations. Belimumab was recently approved as add-on therapy in autoantibody-positive SLE patients with high disease activity unresponsive to standard treatment. Short-term induction pulse therapy with low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide, as well as continued mycophenolate mofetil treatment are advances in lupus nephritis.
Conclusion: The long-term prognosis for SLE has improved markedly in recent decades because of earlier diagnosis and optimized treatment. Further research and randomized controlled trials are needed for the development of specifically targeted therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical and immunologic patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. The European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1993;72:113–124. - PubMed
-
- Fischer-Betz R, Herzer P, Schneider M. Systemischer Lupus erythematodes. [Systemic lupus erythematosus] Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2005;130:2451–2458. - PubMed
-
- Brinks R, Fischer-Betz R, Sander O, Richter JG, Chehab G, Schneider M. Age-specific prevalence of diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus in Germany 2002 and projection to 2030. Lupus. 2014;23:1407–1411. - PubMed
-
- Chehab G, Fischer-Betz R, Schneider M. Entwicklung von Mortalität und Morbidität beim systemischen Lupus erythematodes. Changes in mortality and morbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus] [Z Rheumatol. 2011;70:480–485. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 10-year period: a comparison of early and late manifestations in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2003;82:299–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

