Integrated network analysis and logistic regression modeling identify stage-specific genes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 26179909
- PMCID: PMC4502639
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-015-0114-0
Integrated network analysis and logistic regression modeling identify stage-specific genes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is associated with substantial mortality and morbidity but, OSCC can be difficult to detect at its earliest stage due to its molecular complexity and clinical behavior. Therefore, identification of key gene signatures at an early stage will be highly helpful.
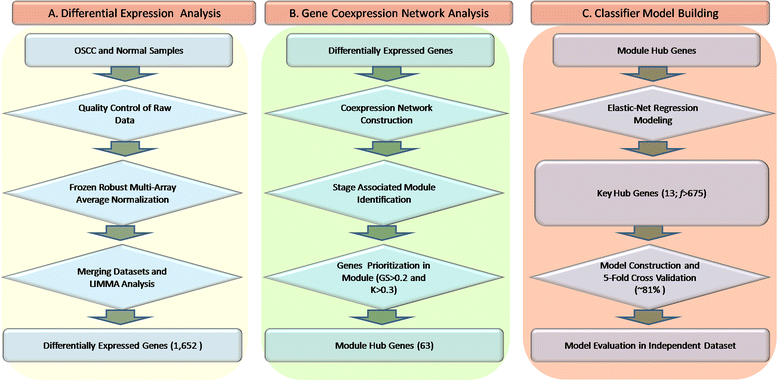
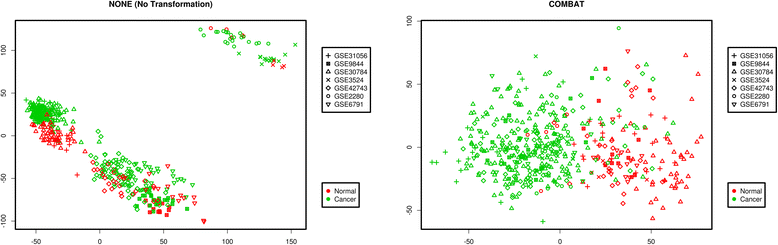
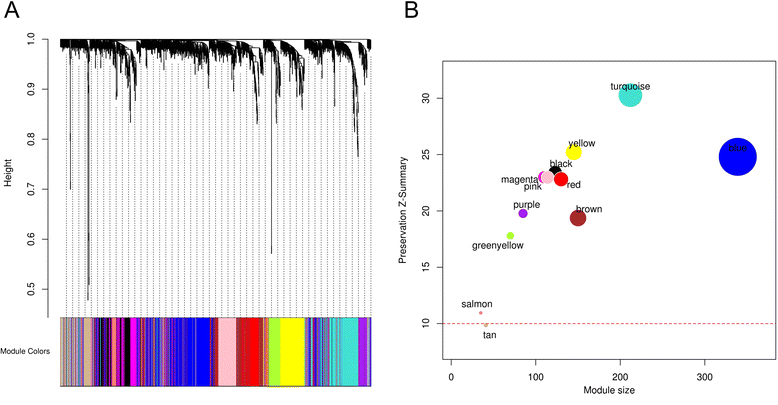
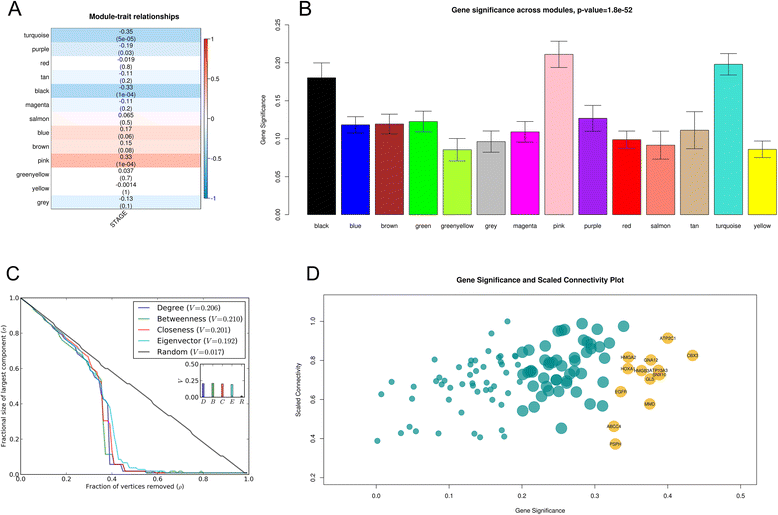
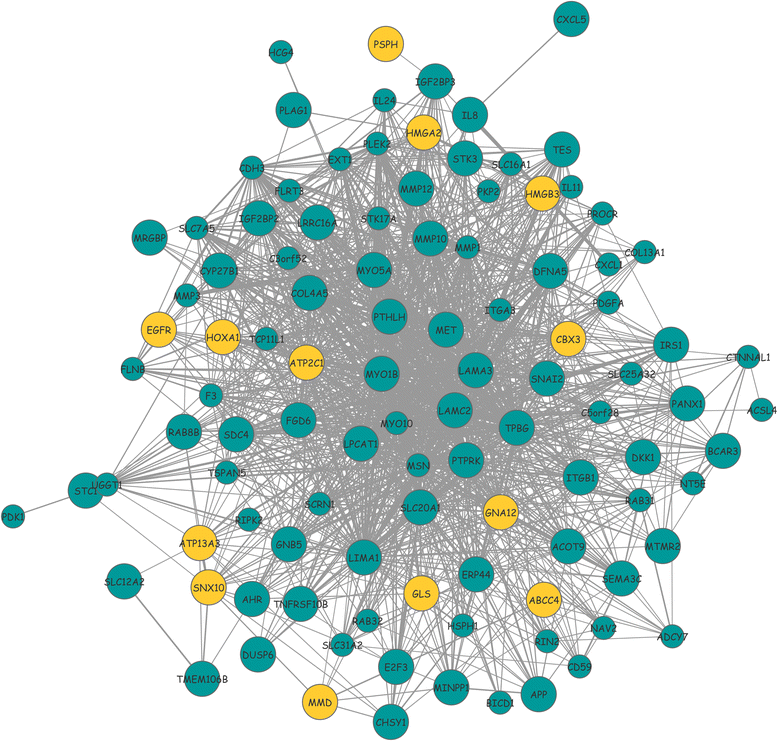
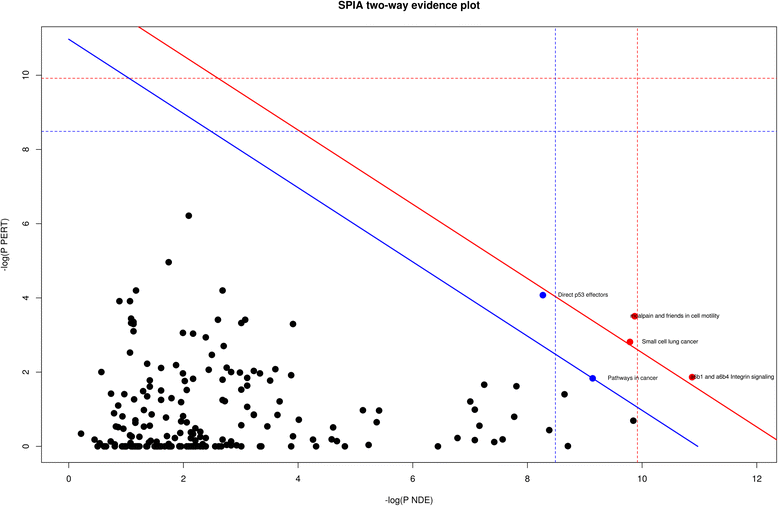
Methods: The aim of this study was to identify key genes associated with progression of OSCC stages. Gene expression profiles were classified into cancer stage-related modules, i.e., groups of genes that are significantly related to a clinical stage. For prioritizing the candidate genes, analysis was further restricted to genes with high connectivity and a significant association with a stage. To assess predictive power of these genes, a classification model was also developed and tested by 5-fold cross validation and on an independent dataset.
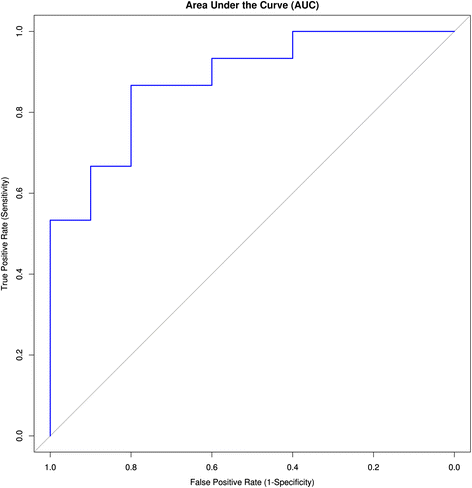
Results: The identified genes were enriched for significant processes and functional pathways, and various genes were found to be directly implicated in OSCC. Forward and stepwise, multivariate logistic regression analyses identified 13 key genes whose expression discriminated early- and late-stage OSCC with predictive accuracy (area under curve; AUC) of ~0.81 in a 5-fold cross-validation strategy.
Conclusions: The proposed network-driven integrative analytical approach can identify multiple genes significantly related to an OSCC stage; the classification model that is developed with these genes may help to distinguish cancer stages. The proposed genes and model hold promise for monitoring of OSCC stage progression, and our findings may facilitate cancer detection at an earlier stage, resulting in improved treatment outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Improving diagnoses of oral cancer. :13–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

