Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: the influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions
- PMID: 26180081
- PMCID: PMC4724176
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nov125
Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: the influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions
Abstract
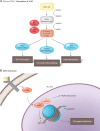
A defining hallmark of glioblastoma is altered tumor metabolism. The metabolic shift towards aerobic glycolysis with reprogramming of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, regardless of oxygen availability, is a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect. In addition to the Warburg effect, glioblastoma tumor cells also utilize the tricarboxylic acid cycle/oxidative phosphorylation in a different capacity than normal tissue. Altered metabolic enzymes and their metabolites are oncogenic and not simply a product of tumor proliferation. Here we highlight the advantages of why tumor cells, including glioblastoma cells, require metabolic reprogramming and how tumor metabolism can converge on tumor epigenetics and unanswered questions in the field.
Keywords: Warburg effect; epigenetics; metabolic reprogramming; molecular signaling.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel GJ. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects. 6th ed Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 1999.
-
- Siegel GJ. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects. 7th ed Amsterdam and Boston: Elsevier; 2006.
-
- Belanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 2011;14(6):724–738. - PubMed
-
- Herrero-Mendez A, Almeida A, Fernandez E, et al. The bioenergetic and antioxidant status of neurons is controlled by continuous degradation of a key glycolytic enzyme by APC/C-Cdh1. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(6):747–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

