Moyamoya Syndrome: A Window of Moyamoya Disease
- PMID: 26180607
- PMCID: PMC4502236
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.6.408
Moyamoya Syndrome: A Window of Moyamoya Disease
Abstract
Moyamoya-like vasculopathy develops in association with various systemic diseases and conditions, which is termed moyamoya syndrome. Relatively common diseases and conditions are related to moyamoya syndrome, including neurofibromatosis type 1, Down syndrome, thyroid disease, and cranial irradiation. Moyamoya syndrome shares phenotypical characteristics with idiopathic moyamoya disease. However, they differ in other details, including clinical presentations, natural history, and treatment considerations. The study of moyamoya syndrome can provide clinicians and researchers with valuable knowledge and insight. Although it is infrequently encountered in clinical practice, moyamoya-like vasculopathy can severely complicate outcomes for patients with various underlying diseases when the clinician fails to expect or diagnose moyamoya syndrome development. Furthermore, moyamoya syndrome could be used as a doorway to more enigmatic moyamoya disease in research. More comprehensive survey and investigation are required to uncover the secrets of all the moyamoya-like phenomena.
Keywords: Down syndrome; Moyamoya syndrome; Neurofibromatosis; Radiation; Thyroid disease.
Figures
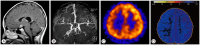
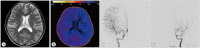
References
-
- Berk AT, Saatci AO, Erçal MD, Tunç M, Ergin M. Ocular findings in 55 patients with Down's syndrome. Ophthalmic Genet. 1996;17:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Booth F, Yanofsky R, Ross IB, Lawrence P, Oen K. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome with moyamoya-like vascular changes. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1999;31:45–48. - PubMed
-
- Bowers DC, Liu Y, Leisenring W, McNeil E, Stovall M, Gurney JG, et al. Late-occurring stroke among long-term survivors of childhood leukemia and brain tumors : a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5277–5282. - PubMed
-
- Cairns AG, North KN. Cerebrovascular dysplasia in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:1165–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

