Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Associations With Pathological Complete Response and Event-Free Survival in HER2-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Treated With Lapatinib and Trastuzumab: A Secondary Analysis of the NeoALTTO Trial
- PMID: 26181252
- PMCID: PMC5551492
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0830
Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Associations With Pathological Complete Response and Event-Free Survival in HER2-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Treated With Lapatinib and Trastuzumab: A Secondary Analysis of the NeoALTTO Trial
Erratum in
-
Error in Figure. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Associations With Pathological Complete Response and Event-Free Survival in HER2-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Treated With Lapatinib and Trastuzumab: A Secondary Analysis of the NeoALTTO Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Jul;1(4):544. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1805. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181274 No abstract available.
-
Misspelled Author Name.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Nov;1(8):1172. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4229. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26562426 No abstract available.
-
Missing Conflict of Interest Disclosure.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;5(1):122. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5678. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30422161 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: The presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is associated with improved outcomes in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive early breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy. The prognostic associations in the neoadjuvant setting of other anti-HER2 agents and combinations are unknown.
Objective: To determine associations between presence of TILs, pathological complete response (pCR), and event-free survival (EFS) end points in patients with early breast cancer treated with trastuzumab, lapatinib, or the combination.
Design, setting, and participants: The NeoALTTO trial (Neoadjuvant Lapatinib and/or Trastuzumab Treatment Optimization) randomly assigned 455 women with HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer between January 5, 2008, and May 27, 2010, to 1 of 3 neoadjuvant treatment arms: trastuzumab, lapatinib, or the combination for 6 weeks followed by the addition of weekly paclitaxel for 12 weeks, followed by 3 cycles of fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide after surgery. The primary end point used in this study was pCR in the breast and lymph nodes, with a secondary end point of EFS. We evaluated levels of percentage of TILs using hematoxylin-eosin-stained core biopsy sections taken at diagnosis (prior to treatment) in a prospectively defined retrospective analysis.
Main outcomes and measures: Levels of TILs were examined for their associations with efficacy end points adjusted for prognostic clinicopathological factors including PIK3CA genotype.
Results: Of the 455 patients, 387 (85.1%) tumor samples were used for the present analysis. The median (interquartile range [IQR]) level of TILs was 12.5% (5.0%-30.0%), with levels lower in hormone receptor-positive (10.0% [5.0%-22.5%]) vs hormone receptor-negative (12.5% [3.0%-35.0%]) samples (P = .02). For the pCR end point, levels of TILs greater than 5% were associated with higher pCR rates independent of treatment group (adjusted odds ratio, 2.60 [95% CI, 1.26-5.39]; P = .01). With a median (IQR) follow-up time of 3.77 (3.50-4.22) years, every 1% increase in TILs was associated with a 3% decrease in the rate of an event (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .002) across all treatment groups.
Conclusions and relevance: The presence of TILs at diagnosis is an independent, positive, prognostic marker in HER2-positive early breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant anti-HER2 agents and chemotherapy for both pCR and EFS end points.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00553358.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
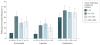
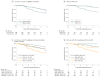
Comment in
-
The Dual Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Primary Breast Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin?JAMA Oncol. 2015 Jul;1(4):455-6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0851. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181253 No abstract available.
-
Failure to Accurately Disclose Conflicts of Interest in Articles Published in JAMA Oncology.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;5(1):118-119. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5674. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30422162 No abstract available.
References
-
- Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(1):105–113. - PubMed
-
- Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) indicate trastuzumab benefit in early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer (HER2+ BC) Cancer Res. 2013;73(24 suppl) Abstract S1-05.
-
- Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(8):1544–1550. - PubMed
-
- Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(7):860–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

