Modulation of p38 kinase by DUSP4 is important in regulating cardiovascular function under oxidative stress
- PMID: 26184564
- PMCID: PMC4684778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.07.013
Modulation of p38 kinase by DUSP4 is important in regulating cardiovascular function under oxidative stress
Abstract
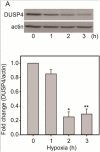
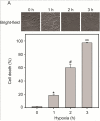
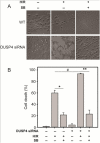
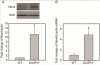
Over-activation of p38 is implicated in many cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including myocardial infarction, hypertrophy, heart failure, and ischemic heart disease. Numerous therapeutic interventions for CVDs have been directed toward the inhibition of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation that contributes to the detrimental effect after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injuries. However, the efficacy of these treatments is far from ideal, as they lack specificity and are associated with high toxicity. Previously, we demonstrated that N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) pretreatment up-regulates DUSP4 expression in endothelial cells, regulating p38 and ERK1/2 activities, and thus providing a protective effect against oxidative stress. Here, endothelial cells under hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) insult and isolated heart I/R injury were used to investigate the role of DUSP4 in the modulation of the p38 pathway. In rat endothelial cells, DUSP4 is time-dependently degraded by H/R (0.25 ± 0.07-fold change of control after 2h H/R). Its degradation is closely associated with hyperphosphorylation of p38 (2.1 ± 0.36-fold change) and cell apoptosis, as indicated by the increase in cells immunopositive for cleaved caspase-3 (12.59 ± 3.38%) or TUNEL labeling (29.46 ± 3.75%). The inhibition of p38 kinase activity with 20 µM SB203580 during H/R prevents H/R-induced apoptosis, assessed via TUNEL (12.99 ± 1.89%). Conversely, DUSP4 gene silencing in endothelial cells augments their sensitivity to H/R-induced apoptosis (45.81 ± 5.23%). This sensitivity is diminished via the inhibition of p38 activity (total apoptotic cells drop to 17.47 ± 1.45%). Interestingly, DUSP4 gene silencing contributes to the increase in superoxide generation from cells. Isolated Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts were subjected to global I/R injury. DUSP4(-/-) hearts had significantly larger infarct size than WT. The increase in I/R-induced infarct in DUSP4(-/-) mice significantly correlates with reduced functional recovery (assessed by RPP%, LVDP%, HR%, and dP/dtmax) as well as lower CF% and a higher initial LVEDP. From immunoblotting analysis, it is evident that p38 is significantly overactivated in DUSP4(-/-) mice after I/R injury. The activation of cleaved caspase-3 is seen in both WT and DUSP4(-/-) I/R hearts. Infusion of a p38 inhibitor prior to ischemia and during the reperfusion improves both WT and DUSP4(-/-) cardiac function. Therefore, the identification of p38 kinase modulation by DUSP4 provides a novel therapeutic target for oxidant-induced diseases, especially myocardial infarction.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; DUSP4; H/R; I/R; MAPK; Oxidative stress; p38.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 4 Overexpression in Cells Prevents Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis via the Upregulation of eNOS.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Apr 24;4:22. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00022. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28484701 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase enhances Ischemia/Reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiac myocytes and exaggerates reperfusion injury in isolated perfused heart.Circ Res. 2000 Mar 31;86(6):692-9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.86.6.692. Circ Res. 2000. PMID: 10747006
-
Luteolin inhibits ROS-activated MAPK pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Life Sci. 2015 Feb 1;122:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.11.014. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25476833
-
Role of p38 inhibition in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 May;68(5):513-24. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1193-2. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22205273 Review.
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: a critical node linking insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Mar;9(1):38-46. doi: 10.2174/187153009787582397. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19275680 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles Released by Human Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Promote Angiogenesis.Front Physiol. 2018 Dec 14;9:1794. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01794. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30618806 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, acute stroke, acute kidney injury and delirium after cardiac surgery - a sub-analysis of the RIPHeart-Study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Jan 24;19(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1002-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 30678657 Free PMC article.
-
Dioxygen and Metabolism; Dangerous Liaisons in Cardiac Function and Disease.Front Physiol. 2017 Dec 12;8:1044. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01044. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29311974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of microRNA-122 alleviates pyroptosis by targeting dual-specificity phosphatase 4 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 13;9(7):e18238. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18238. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539226 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 4 Overexpression in Cells Prevents Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis via the Upregulation of eNOS.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Apr 24;4:22. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00022. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28484701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendis S, Puska P, Norrving B, World Health Organization. World Heart Federation. World Stroke Organization . Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control. World Health Organization in collaboration with the World Heart Federation and the World Stroke Organization; Geneva: 2011.
-
- Zweier JL, Talukder MA. The role of oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Aune SE, Yeh ST, Zelinski DP, Angelos MG. Measurement of hydrogen peroxide and oxidant stress in a recirculating whole blood-perfused rat heart model. Resuscitation. 2011;82:222–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

