Bacillithiol: a key protective thiol in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 26184907
- PMCID: PMC4914364
- DOI: 10.1586/14787210.2015.1064309
Bacillithiol: a key protective thiol in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
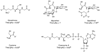
Bacillithiol is a low-molecular-weight thiol analogous to glutathione and is found in several Firmicutes, including Staphylococcus aureus. Since its discovery in 2009, bacillithiol has been a topic of interest because it has been found to contribute to resistance during oxidative stress and detoxification of electrophiles, such as the antibiotic fosfomycin, in S. aureus. The rapid increase in resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to available therapeutic agents is a great health concern, and many research efforts are focused on identifying new drugs and targets to combat this organism. This review describes the discovery of bacillithiol, studies that have elucidated the physiological roles of this molecule in S. aureus and other Bacilli, and the contribution of bacillithiol to S. aureus fitness during pathogenesis. Additionally, the bacillithiol biosynthesis pathway is evaluated as a novel drug target that can be utilized in combination with existing therapies to treat S. aureus infections.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; bacillithiol; bacillithiol conjugate amidase; drug resistance; fosfomycin; oxidative stress; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Kit Pogliano is a founder of Linnaeus Bioscience Incorporated, holds equity interest in the company and receives consulting income. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures








References
-
-
Fahey RC. Glutathione analogs in prokaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(5):3182–3198. • A comprehensive review of bacterial low molecular weight thiols.
-
-
- Keire DA, Robert JM, Rabenstein DL. Microscopic Protonation equilibria and solution conformations of coenzyme-a and coenzyme-a disulfides. J Org Chem. 1992;57(16):4427–4431.
-
- Benesch RE, Benesch R. The acid strength of the -Sh group in cysteine and related compounds. J Am Chem Soc. 1955;77(22):5877–5881.
-
- Rabenstein DL. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the acid-base chemistry of amino acids and peptides. I. Microscopic ionization constants of glutathione and methylmercury-complexed glutathione. J Am Chem Soc. 1973;95(9):2797–2803.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
