The Kinesio Taping Method for Myofascial Pain Control
- PMID: 26185522
- PMCID: PMC4491400
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/950519
The Kinesio Taping Method for Myofascial Pain Control
Abstract
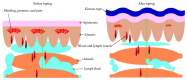
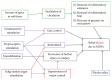
Many people continue suffering from myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) defined as a regional pain syndrome characterized by muscle pain caused by myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) clinically. Muscle spasm and block of blood circulation can be noticed in the taut bands. In the MTrP region, nociceptors can be sensitized by the peripheral inflammatory factors and contracture of fascia can also be induced. Traditional treatments of MPS include stretching therapy, thermal treatment, electrical stimulation, massage, manipulation, trigger points injection, acupuncture, and medicine. However, the pain syndrome may not be relieved even under multiple therapies. Recently, the Kinesio Taping (KT) method is popularly used in sports injuries, postoperative complications, and various pain problems, but little research is focused on MPS with KT method. In this paper, we review the research studies on the application to KT in treating MPS and other related issues. It appears that the KT application can elevate the subcutaneous space and then increase the blood circulation and lymph fluid drainage to reduce the chemical factors around the MTrP region. Therefore, it is suggested that KT method can be used as a regular treatment or added to the previous treatment for myofascial pain.
Figures
References
-
- Travell J. G., Simons D. G. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual. Vol. 1. Baltimore, Md, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1983.
-
- Hong C.-Z. Myofascial pain therapy. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain. 2004;12(3-4):37–43. doi: 10.1300/J094v12n03_06. - DOI
-
- Cailliet R. Soft Tissue Pain and Disability. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: F.A. Davis Company; 1977.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

