Fetal programming of polycystic ovary syndrome
- PMID: 26185601
- PMCID: PMC4499527
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i7.936
Fetal programming of polycystic ovary syndrome
Abstract
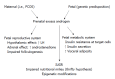
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects up to 6.8% of reproductive age women. Experimental research and clinical observations suggest that PCOS may originate in the very early stages of development, possibly even during intrauterine life. This suggests that PCOS is either genetically-transmitted or is due to epigenetic alterations that develop in the intrauterine microenvironment. Although familial cases support the role of genetic factors, no specific genetic pattern has been defined in PCOS. Several candidate genes have been implicated in its pathogenesis, but none can specifically be implicated in PCOS development. Hypotheses based on the impact of the intrauterine environment on PCOS development can be grouped into two categories. The first is the "thrifty" phenotype hypothesis, which states that intrauterine nutritional restriction in fetuses causes decreased insulin secretion and, as a compensatory mechanism, insulin resistance. Additionally, an impaired nutritional environment can affect the methylation of some specific genes, which can also trigger PCOS. The second hypothesis postulates that fetal exposure to excess androgen can induce changes in differentiating tissues, causing the PCOS phenotype to develop in adult life. This review aimed to examine the role of fetal programming in development of PCOS.
Keywords: Androgens; Fetal programming; Genetic; Intrauterine growth retardation; Polycystic ovary syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Ehrmann DA. Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1223–1236. - PubMed
-
- Ibáñez L, Potau N, Francois I, de Zegher F. Precocious pubarche, hyperinsulinism, and ovarian hyperandrogenism in girls: relation to reduced fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:3558–3562. - PubMed
-
- Sir-Petermann T, Hitchsfeld C, Maliqueo M, Codner E, Echiburú B, Gazitúa R, Recabarren S, Cassorla F. Birth weight in offspring of mothers with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Hum Reprod. 2005;20:2122–2126. - PubMed
-
- Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Piperi C, Spina J, Argyrakopoulou G, Papanastasiou L, Bergiele A, Panidis D. Polycystic ovary syndrome: the influence of environmental and genetic factors. Hormones (Athens) 2006;5:17–34. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources