Topiramate-induced nephrolithiasis
- PMID: 26185660
- PMCID: PMC4498874
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.275
Topiramate-induced nephrolithiasis
Abstract
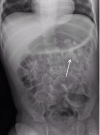
Nephrolithiasis is a less common side effect of the antiepileptic drug topiramate. We report the case of a 3-year-old boy who presented to the emergency department with abdominal pain; examinations revealed a large calcification in the left kidney. Regular ultrasound examinations are recommended in children using topiramate.
Keywords: Abdominal pain; calcification; epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Vega D, Maalouf NM. Sakhaee K. Increased propensity for calcium phosphate kidney stones with topiramate use. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2007;6:547–557. - PubMed
-
- Mahmoud AA, Rizk T, El-Bakri NK, Riaz M, Dannawi S. Al Tannir M. Incidence of kidney stones with topiramate treatment in pediatric patients. Epilepsia. 2011;52:1890–1893. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources