IFI16 Expression Is Related to Selected Transcription Factors during B-Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 26185770
- PMCID: PMC4491573
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/747645
IFI16 Expression Is Related to Selected Transcription Factors during B-Cell Differentiation
Abstract
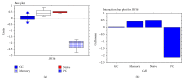
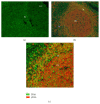
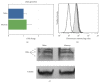
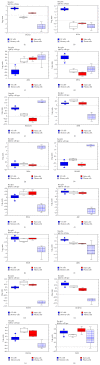
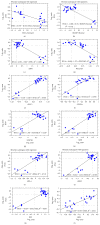
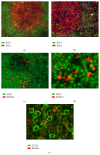
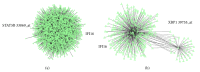
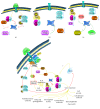
The interferon-inducible DNA sensor IFI16 is involved in the modulation of cellular survival, proliferation, and differentiation. In the hematopoietic system, IFI16 is consistently expressed in the CD34+ stem cells and in peripheral blood lymphocytes; however, little is known regarding its regulation during maturation of B- and T-cells. We explored the role of IFI16 in normal B-cell subsets by analysing its expression and relationship with the major transcription factors involved in germinal center (GC) development and plasma-cell (PC) maturation. IFI16 mRNA was differentially expressed in B-cell subsets with significant decrease in IFI16 mRNA in GC and PCs with respect to naïve and memory subsets. IFI16 mRNA expression is inversely correlated with a few master regulators of B-cell differentiation such as BCL6, XBP1, POU2AF1, and BLIMP1. In contrast, IFI16 expression positively correlated with STAT3, REL, SPIB, RELA, RELB, IRF4, STAT5B, and STAT5A. ARACNE algorithm indicated a direct regulation of IFI16 by BCL6, STAT5B, and RELB, whereas the relationship between IFI16 and the other factors is modulated by intermediate factors. In addition, analysis of the CD40 signaling pathway showed that IFI16 gene expression directly correlated with NF-κB activation, indicating that IFI16 could be considered an upstream modulator of NF-κB in human B-cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IRF4 negatively regulates proliferation of germinal center B cell-derived Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines and induces differentiation toward plasma cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;86(10):581-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.05.006. Epub 2007 Jul 24. Eur J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17651861
-
CD40, but not lipopolysaccharide and anti-IgM stimulation of primary B lymphocytes, leads to a persistent nuclear accumulation of RelB.J Immunol. 1996 Dec 1;157(11):4862-9. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8943389
-
BRAD4 plays a critical role in germinal center response by regulating Bcl-6 and NF-κB activation.Cell Immunol. 2015 Mar;294(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.01.010. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Cell Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25656449
-
Regulatory mechanisms that determine the development and function of plasma cells.Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:205-30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141138. Epub 2001 Dec 19. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12524387 Review.
-
Blimp1: driving terminal differentiation to a T.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;780:85-100. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-5632-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21842367 Review.
Cited by
-
EMCV VP2 degrades IFI16 through Caspase-dependent apoptosis to evade IFI16-STING pathway.Virol J. 2024 Nov 18;21(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02568-8. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39551733 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation in chronic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Aug 13;26(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03916-0. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40804668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage-Induced Inflammatory Microenvironment and Adult Stem Cell Response.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 8;9:729136. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.729136. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34692684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 16 (IFI16) Has a Broad-Spectrum Binding Ability Against ssDNA Targets: An Evolutionary Hypothesis for Antiretroviral Checkpoint.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 4;10:1426. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01426. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31333597 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of Interferon-inducible protein 16 contributes to psoriasis by modulating chemokine production in keratinocytes.Sci Rep. 2016 May 3;6:25381. doi: 10.1038/srep25381. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27137868 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

