Different Effects of BORIS/CTCFL on Stemness Gene Expression, Sphere Formation and Cell Survival in Epithelial Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 26185996
- PMCID: PMC4506091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132977
Different Effects of BORIS/CTCFL on Stemness Gene Expression, Sphere Formation and Cell Survival in Epithelial Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
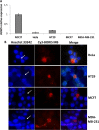
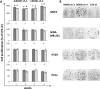
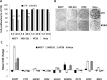
Cancer stem cells are cancer cells characterized by stem cell properties and represent a small population of tumor cells that drives tumor development, progression, metastasis and drug resistance. To date, the molecular mechanisms that generate and regulate cancer stem cells are not well defined. BORIS (Brother of Regulator of Imprinted Sites) or CTCFL (CTCF-like) is a DNA-binding protein that is expressed in normal tissues only in germ cells and is re-activated in tumors. Recent evidences have highlighted the correlation of BORIS/CTCFL expression with poor overall survival of different cancer patients. We have previously shown an association of BORIS-expressing cells with stemness gene expression in embryonic cancer cells. Here, we studied the role of BORIS in epithelial tumor cells. Using BORIS-molecular beacon that was already validated, we were able to show the presence of BORIS mRNA in cancer stem cell-enriched populations (side population and spheres) of cervical, colon and breast tumor cells. BORIS silencing studies showed a decrease of sphere formation capacity in breast and colon tumor cells. Importantly, BORIS-silencing led to down-regulation of hTERT, stem cell (NANOG, OCT4, SOX2 and BMI1) and cancer stem cell markers (ABCG2, CD44 and ALDH1) genes. Conversely, BORIS-induction led to up-regulation of the same genes. These phenotypes were observed in cervical, colon and invasive breast tumor cells. However, a completely different behavior was observed in the non-invasive breast tumor cells (MCF7). Indeed, these cells acquired an epithelial mesenchymal transition phenotype after BORIS silencing. Our results demonstrate that BORIS is associated with cancer stem cell-enriched populations of several epithelial tumor cells and the different phenotypes depend on the origin of tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001. November 1;414(6859):105–11. - PubMed
-
- Dalerba P, Cho RW, Clarke MF. Cancer stem cells: models and concepts. Annual review of medicine. 2007;58:267–84. - PubMed
-
- Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M. Cancer stem cells. The New England journal of medicine. 2006. September 21;355(12):1253–61. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nature medicine. 1997. July;3(7):730–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

