The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome
- PMID: 26186194
- PMCID: PMC4617211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.043
The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome
Abstract
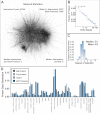
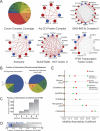
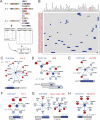
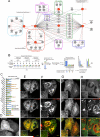
Protein interactions form a network whose structure drives cellular function and whose organization informs biological inquiry. Using high-throughput affinity-purification mass spectrometry, we identify interacting partners for 2,594 human proteins in HEK293T cells. The resulting network (BioPlex) contains 23,744 interactions among 7,668 proteins with 86% previously undocumented. BioPlex accurately depicts known complexes, attaining 80%-100% coverage for most CORUM complexes. The network readily subdivides into communities that correspond to complexes or clusters of functionally related proteins. More generally, network architecture reflects cellular localization, biological process, and molecular function, enabling functional characterization of thousands of proteins. Network structure also reveals associations among thousands of protein domains, suggesting a basis for examining structurally related proteins. Finally, BioPlex, in combination with other approaches, can be used to reveal interactions of biological or clinical significance. For example, mutations in the membrane protein VAPB implicated in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis perturb a defined community of interactors.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Babu M, Vlasblom J, Pu S, Guo X, Graham C, Bean BD, Burston HE, Vizeacoumar FJ, Snider J, Phanse S, et al. Interaction landscape of membrane-protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 2012;489:585–589. - PubMed
-
- Barabasi AL, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999;286:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: a Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B. 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

