Targeting glutaminolysis has antileukemic activity in acute myeloid leukemia and synergizes with BCL-2 inhibition
- PMID: 26186940
- PMCID: PMC4608389
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-01-621870
Targeting glutaminolysis has antileukemic activity in acute myeloid leukemia and synergizes with BCL-2 inhibition
Abstract
Cancer cells require glutamine to adapt to increased biosynthetic activity. The limiting step in intracellular glutamine catabolism involves its conversion to glutamate by glutaminase (GA). Different GA isoforms are encoded by the genes GLS1 and GLS2 in humans. Herein, we show that glutamine levels control mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Glutaminase C (GAC) is the GA isoform that is most abundantly expressed in AML. Both knockdown of GLS1 expression and pharmacologic GLS1 inhibition by the drug CB-839 can reduce OXPHOS, leading to leukemic cell proliferation arrest and apoptosis without causing cytotoxic activity against normal human CD34(+) progenitors. Strikingly, GLS1 knockdown dramatically inhibited AML development in NSG mice. The antileukemic activity of CB-839 was abrogated by both the expression of a hyperactive GAC(K320A) allele and the addition of the tricarboxyclic acid cycle product α-ketoglutarate, indicating the critical function of GLS1 in AML cell survival. Finally, glutaminolysis inhibition activated mitochondrial apoptosis and synergistically sensitized leukemic cells to priming with the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199. These findings show that targeting glutamine addiction via GLS1 inhibition offers a potential novel therapeutic strategy for AML.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
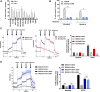
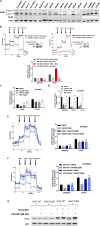


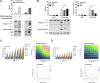
Comment in
-
Exploiting AML vulnerability: glutamine dependency.Blood. 2015 Sep 10;126(11):1269-70. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-659508. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26359432 No abstract available.
References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123(3191):309–314. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Sánchez R, Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Marín-Hernández A, Saavedra E. Energy metabolism in tumor cells. FEBS J. 2007;274(6):1393–1418. - PubMed
-
- Curthoys NP, Watford M. Regulation of glutaminase activity and glutamine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1995;15:133–159. - PubMed
-
- Elgadi KM, Meguid RA, Qian M, Souba WW, Abcouwer SF. Cloning and analysis of unique human glutaminase isoforms generated by tissue-specific alternative splicing. Physiol Genomics. 1999;1(2):51–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

