Salmonella Infection Drives Promiscuous B Cell Activation Followed by Extrafollicular Affinity Maturation
- PMID: 26187411
- PMCID: PMC4523395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.013
Salmonella Infection Drives Promiscuous B Cell Activation Followed by Extrafollicular Affinity Maturation
Abstract
The B cell response to Salmonella typhimurium (STm) occurs massively at extrafollicular sites, without notable germinal centers (GCs). Little is known in terms of its specificity. To expand the knowledge of antigen targets, we screened plasmablast (PB)-derived monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for Salmonella specificity, using ELISA, flow cytometry, and antigen microarray. Only a small fraction (0.5%-2%) of the response appeared to be Salmonella-specific. Yet, infection of mice with limited B cell receptor (BCR) repertoires impaired the response, suggesting that BCR specificity was important. We showed, using laser microdissection, that somatic hypermutation (SHM) occurred efficiently at extrafollicular sites leading to affinity maturation that in turn led to detectable STm Ag-binding. These results suggest a revised vision of how clonal selection and affinity maturation operate in response to Salmonella. Clonal selection initially is promiscuous, activating cells with virtually undetectable affinity, yet SHM and selection occur during the extrafollicular response yielding higher affinity, detectable antibodies.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
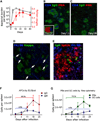

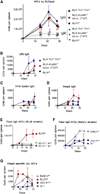
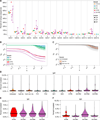
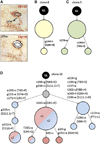
Comment in
-
Caught Off Center: Rethinking the Requirements for Antibody Affinity Maturation.Immunity. 2015 Jul 21;43(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.002. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26200006
References
-
- Alamyar E, Duroux P, Lefranc MP, Giudicelli V. IMGT(®) tools for the nucleotide analysis of immunoglobulin (IG) and T cell receptor (TR) V-(D)-J repertoires, polymorphisms, and IG mutations: IMGT/V-QUEST and IMGT/HighV-QUEST for NGS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012;882:569–604. - PubMed
-
- Bobat S, Flores-Langarica A, Hitchcock J, Marshall JL, Kingsley RA, Goodall M, Gil-Cruz C, Serre K, Leyton DL, Letran SE, et al. Soluble flagellin, FliC, induces an Ag-specific Th2 response, yet promotes T-bet-regulated Th1 clearance of Salmonella typhimurium infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011;41:1606–1618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T15 LM007056/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056172/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073722/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T15-LM07056/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104739/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105018/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR044077/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI043603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI104739/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI 073722/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

