Effect of olfactory manganese exposure on anxiety-related behavior in a mouse model of iron overload hemochromatosis
- PMID: 26189056
- PMCID: PMC4522346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.016
Effect of olfactory manganese exposure on anxiety-related behavior in a mouse model of iron overload hemochromatosis
Abstract
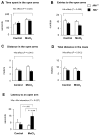
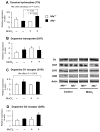
Manganese in excess promotes unstable emotional behavior. Our previous study showed that olfactory manganese uptake into the brain is altered in Hfe(-/-) mice, a model of iron overload hemochromatosis, suggesting that Hfe deficiency could modify the neurotoxicity of airborne manganese. We determined anxiety-related behavior and monoaminergic protein expression after repeated intranasal instillation of MnCl2 to Hfe(-/-) mice. Compared with manganese-instilled wild-type mice, Hfe(-/-) mice showed decreased manganese accumulation in the cerebellum. Hfe(-/-) mice also exhibited increased anxiety with decreased exploratory activity and elevated dopamine D1 receptor and norepinephrine transporter in the striatum. Moreover, Hfe deficiency attenuated manganese-associated impulsivity and modified the effect of manganese on the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase, vesicular monoamine transporter and serotonin transporter. Together, our data indicate that loss of HFE function alters manganese-associated emotional behavior and further suggest that HFE could be a potential molecular target to alleviate affective disorders induced by manganese inhalation.
Keywords: Dopamine; Elevated plus maze; Impulsivity; Intranasal instillation; Norepinephrine; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
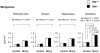
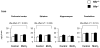
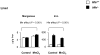
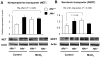

Similar articles
-
Absorption of manganese and iron in a mouse model of hemochromatosis.PLoS One. 2013 May 21;8(5):e64944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064944. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23705020 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation in HFE gene decreases manganese accumulation and oxidative stress in the brain after olfactory manganese exposure.Metallomics. 2016 Jun 1;8(6):618-27. doi: 10.1039/c6mt00080k. Metallomics. 2016. PMID: 27295312 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of hfe function reverses impaired recognition memory caused by olfactory manganese exposure in mice.Toxicol Res. 2015 Mar;31(1):17-23. doi: 10.5487/TR.2015.31.1.017. Toxicol Res. 2015. PMID: 25874029 Free PMC article.
-
[HFE hemochromatosis: pathogenic and diagnostic approach].Transfus Clin Biol. 2005 Jun;12(2):77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tracli.2005.04.040. Transfus Clin Biol. 2005. PMID: 15925529 Review. French.
-
[Genetic hemochromatosis and the HFE gene: from molecular genetics to clinical diagnosis].Z Gastroenterol. 2000 Jun;38(6):509-15. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-14891. Z Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 10923364 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Combined exposure to methylmercury and manganese during L1 larval stage causes motor dysfunction, cholinergic and monoaminergic up-regulation and oxidative stress in L4 Caenorhabditis elegans.Toxicology. 2019 Jan 1;411:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Toxicology. 2019. PMID: 30336192 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Manganese Exposure Modifies the Translation Machinery via PI3K/Akt Signaling in Glial Cells.ASN Neuro. 2022 Jan-Dec;14:17590914221131452. doi: 10.1177/17590914221131452. ASN Neuro. 2022. PMID: 36203371 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of iron metabolism on manganese transport and toxicity.Metallomics. 2017 Aug 16;9(8):1028-1046. doi: 10.1039/c7mt00079k. Metallomics. 2017. PMID: 28620665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAC128 mouse model of Huntington disease is protected against subtle chronic manganese (Mn)-induced behavioral and neuropathological changes.Neurotoxicology. 2021 Dec;87:94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.09.002. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Neurotoxicology. 2021. PMID: 34543681 Free PMC article.
-
Brain iron loading impairs DNA methylation and alters GABAergic function in mice.FASEB J. 2019 Feb;33(2):2460-2471. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801116RR. Epub 2018 Oct 2. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30277817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida SS, Tonkiss J, Galler JR. Prenatal protein malnutrition affects exploratory behavior of female rats in the elevated plus-maze test. Physiol Behav. 1996;60:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JG, Fordahl SC, Cooney PT, Weaver TL, Colyer CL, Erikson KM. Extracellular norepinephrine, norepinephrine receptor and transporter protein and mRNA levels are differentially altered in the developing rat brain due to dietary iron deficiency and manganese exposure. Brain research. 2009;1281:1–14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Archer T, Fredriksson A. Functional consequences of iron overload in catecholaminergic interactions: the Youdim factor. Neurochemical research. 2007;32:1625–1639. - PubMed
-
- Beard JL, Erikson KM, Jones BC. Neurobehavioral analysis of developmental iron deficiency in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2002;134:517–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

