Actin age orchestrates myosin-5 and myosin-6 run lengths
- PMID: 26190073
- PMCID: PMC4556227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.06.033
Actin age orchestrates myosin-5 and myosin-6 run lengths
Abstract
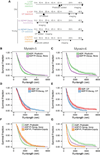
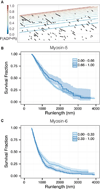
Unlike a static and immobile skeleton, the actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network of filamentous actin (F-actin) polymers that continuously turn over. In addition to generating mechanical forces and sensing mechanical deformation, dynamic F-actin networks serve as cellular tracks for myosin motor traffic. However, much of our mechanistic understanding of processive myosins comes from in vitro studies in which motility was studied on pre-assembled and artificially stabilized, static F-actin tracks. In this work, we examine the role of actin dynamics in single-molecule myosin motility using assembling F-actin and two highly processive motors, myosin-5 and myosin-6. These two myosins have distinct functions in the cell and travel in opposite directions along actin filaments [1-3]. Myosin-5 walks toward the barbed ends of F-actin, traveling to sites of actin polymerization at the cell periphery [4]. Myosin-6 walks toward the pointed end of F-actin [5], traveling toward the cell center along older segments of the actin filament. We find that myosin-5 takes 1.3- to 1.5-fold longer runs on ADP•Pi (young) F-actin, whereas myosin-6 takes 1.7- to 3.6-fold longer runs along ADP (old) F-actin. These results suggest that conformational differences between ADP•Pi and ADP F-actin tailor these myosins to walk farther toward their preferred actin filament end. Taken together, these experiments define a new mechanism by which myosin traffic may sort to different F-actin networks depending on filament age.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The stepping pattern of myosin X is adapted for processive motility on bundled actin.Biophys J. 2010 Sep 22;99(6):1818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.066. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20858426 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin-Specific Adaptations of In vitro Fluorescence Microscopy-Based Motility Assays.J Vis Exp. 2021 Feb 4;(168). doi: 10.3791/62180. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 33616114
-
Myosin and gelsolin cooperate in actin filament severing and actomyosin motor activity.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100181. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015863. Epub 2020 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33303625 Free PMC article.
-
Cargo recognition and cargo-mediated regulation of unconventional myosins.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):3061-70. doi: 10.1021/ar500216z. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25230296 Review.
-
How Actin Tracks Affect Myosin Motors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1239:183-197. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38062-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32451860 Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution structures of the actomyosin-V complex in three nucleotide states provide insights into the force generation mechanism.Elife. 2021 Nov 23;10:e73724. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73724. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34812732 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Mechanisms to Regulate Actin Functions: "Fundamental" Versus Lineage-Specific Mechanisms and Hierarchical Relationships.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 13;15(2):279. doi: 10.3390/biom15020279. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-Hydroxyacetophenone modulates the actomyosin cytoskeleton to reduce metastasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22423-22429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014639117. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32848073 Free PMC article.
-
The actomyosin interface contains an evolutionary conserved core and an ancillary interface involved in specificity.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 25;12(1):1892. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22093-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33767187 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanisms of actin cytoskeleton regulation in cell migration using cryo-EM.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):87-99. doi: 10.1042/BST20220221. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36695514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buss F, Spudich G, Kendrick-Jones J. Myosin VI: cellular functions and motor properties. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:649–676. - PubMed
-
- Sellers JR, Goodson HV. Motor proteins 2: myosin. Protein Profile. 1995;2:1323–1423. - PubMed
-
- Reck-Peterson SL, Provance DW, Mooseker MS, Mercer JA. Class V myosins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1496:36–51. - PubMed
-
- Wells AL, Lin AW, Chen LQ, Safer D, Cain SM, Hasson T, Carragher BO, Milligan RA, Sweeney HL. Myosin VI is an actin-based motor that moves backwards. Nature. 1999;401:505–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

