Antiviral roles of plant ARGONAUTES
- PMID: 26190744
- PMCID: PMC4618181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.06.013
Antiviral roles of plant ARGONAUTES
Abstract
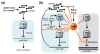
ARGONAUTES (AGOs) are the effector proteins functioning in eukaryotic RNA silencing pathways. AGOs associate with small RNAs and are programmed to target complementary RNA or DNA. Plant viruses induce a potent and specific antiviral RNA silencing host response in which AGOs play a central role. Antiviral AGOs associate with virus-derived small RNAs to repress complementary viral RNAs or DNAs, or with endogenous small RNAs to regulate host gene expression and promote antiviral defense. Here, we review recent progress towards understanding the roles of plant AGOs in antiviral defense. We also discuss the strategies that viruses have evolved to modulate, attenuate or suppress AGO antiviral functions.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest relating to this article.
Figures
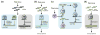
References
-
- Meister G. Argonaute proteins: functional insights and emerging roles. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:447–459. - PubMed
-
- Martinez de Alba AE, Elvira-Matelot E, Vaucheret H. Gene silencing in plants: A diversity of pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1829:1300–1308. - PubMed
-
- Szittya G, Burgyan J. RNA interference-mediated intrinsic antiviral immunity in plants. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;371:153–181. - PubMed
-
- Csorba T, Kontra L, Burgyan J. viral silencing suppressors: Tools forged to fine-tune host-pathogen coexistence. Virology. 2015;479–480:85–103. This interesting review provides an exhaustive compilation of information related to the mechanistic functions of all VSRs identified to date in plant viruses (of special interest are Table 1 and Figure 1) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

