Measurement of the [Formula: see text] production cross-section in proton-proton collisions via the decay [Formula: see text]
Affiliations
- 1 Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 2 Physik-Institut, Universität Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland.
- 3 Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
- 4 H.H. Wills Physics Laboratory, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK.
- 5 Oliver Lodge Laboratory, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK.
- 6 LPC, Clermont Université, Université Blaise Pascal, CNRS/IN2P3, Clermont-Ferrand, France.
- 7 CPPM, Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS/IN2P3, Marseille, France.
- 8 Fakultät Physik, Technische Universität Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany.
- 9 European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland.
- 10 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK.
- 11 Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute (PNPI), Gatchina, Russia.
- 12 Sezione INFN di Roma La Sapienza, Rome, Italy.
- 13 Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 14 Sezione INFN di Padova, Padua, Italy.
- 15 LAL, Université Paris-Sud, CNRS/IN2P3, Orsay, France.
- 16 Center for High Energy Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
- 17 Sezione INFN di Firenze, Florence, Italy.
- 18 University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH USA.
- 19 Sezione INFN di Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy.
- 20 University of Maryland, College Park, MD USA.
- 21 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK.
- 22 Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik (MPIK), Heidelberg, Germany.
- 23 Institute for High Energy Physics (IHEP), Protvino, Russia.
- 24 Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY USA.
- 25 Physikalisches Institut, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany.
- 26 Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK.
- 27 Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 28 Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 29 Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
- 30 National Center for Nuclear Research (NCBJ), Warsaw, Poland.
- 31 Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 32 LAPP, Université de Savoie, CNRS/IN2P3, Annecy-Le-Vieux, France.
- 33 Sezione INFN di Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
- 34 Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas (CBPF), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 35 Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow, Russia.
- 36 LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Université Paris Diderot, CNRS/IN2P3, Paris, France.
- 37 Laboratori Nazionali dell'INFN di Frascati, Frascati, Italy.
- 38 Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University (SINP MSU), Moscow, Russia.
- 39 University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
- 40 Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (SB RAS) and Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia.
- 41 Sezione INFN di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy.
- 42 Sezione INFN di Milano Bicocca, Milan, Italy.
- 43 Sezione INFN di Bologna, Bologna, Italy.
- 44 Sezione INFN di Roma Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy.
- 45 Sezione INFN di Genova, Genoa, Italy.
- 46 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK.
- 47 Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
- 48 Henryk Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kraków, Poland.
- 49 Imperial College London, London, UK.
- 50 Horia Hulubei National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele, Romania.
- 51 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA USA.
- 52 NSC Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology (NSC KIPT), Kharkiv, Ukraine.
- 53 STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, UK.
- 54 Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INR RAN), Moscow, Russia.
- 55 Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, AGH-University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland.
- 56 Sezione INFN di Milano, Milan, Italy.
- 57 Institut für Physik, Universität Rostock, Rostock, Germany.
- 58 Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics, VU University Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 59 National Research Centre Kurchatov Institute, Moscow, Russia.
- 60 Instituto de Fisica Corpuscular (IFIC), Universitat de Valencia-CSIC, Valencia, Spain.
- 61 School of Physics, University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland.
- 62 Institute for Nuclear Research of the National Academy of Sciences (KINR), Kyiv, Ukraine.
- 63 KVI, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 64 Sezione INFN di Bari, Bari, Italy.
- 65 Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey.
- 66 Institute of Particle Physics, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, Hubei China.
- PMID: 26190939
- PMCID: PMC4498677
- DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-015-3502-x
Measurement of the [Formula: see text] production cross-section in proton-proton collisions via the decay [Formula: see text]
Authors
Affiliations
- 1 Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 2 Physik-Institut, Universität Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland.
- 3 Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
- 4 H.H. Wills Physics Laboratory, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK.
- 5 Oliver Lodge Laboratory, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK.
- 6 LPC, Clermont Université, Université Blaise Pascal, CNRS/IN2P3, Clermont-Ferrand, France.
- 7 CPPM, Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS/IN2P3, Marseille, France.
- 8 Fakultät Physik, Technische Universität Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany.
- 9 European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland.
- 10 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK.
- 11 Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute (PNPI), Gatchina, Russia.
- 12 Sezione INFN di Roma La Sapienza, Rome, Italy.
- 13 Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 14 Sezione INFN di Padova, Padua, Italy.
- 15 LAL, Université Paris-Sud, CNRS/IN2P3, Orsay, France.
- 16 Center for High Energy Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
- 17 Sezione INFN di Firenze, Florence, Italy.
- 18 University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH USA.
- 19 Sezione INFN di Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy.
- 20 University of Maryland, College Park, MD USA.
- 21 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK.
- 22 Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik (MPIK), Heidelberg, Germany.
- 23 Institute for High Energy Physics (IHEP), Protvino, Russia.
- 24 Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY USA.
- 25 Physikalisches Institut, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany.
- 26 Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK.
- 27 Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 28 Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 29 Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
- 30 National Center for Nuclear Research (NCBJ), Warsaw, Poland.
- 31 Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 32 LAPP, Université de Savoie, CNRS/IN2P3, Annecy-Le-Vieux, France.
- 33 Sezione INFN di Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
- 34 Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas (CBPF), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 35 Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow, Russia.
- 36 LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Université Paris Diderot, CNRS/IN2P3, Paris, France.
- 37 Laboratori Nazionali dell'INFN di Frascati, Frascati, Italy.
- 38 Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University (SINP MSU), Moscow, Russia.
- 39 University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
- 40 Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (SB RAS) and Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia.
- 41 Sezione INFN di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy.
- 42 Sezione INFN di Milano Bicocca, Milan, Italy.
- 43 Sezione INFN di Bologna, Bologna, Italy.
- 44 Sezione INFN di Roma Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy.
- 45 Sezione INFN di Genova, Genoa, Italy.
- 46 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK.
- 47 Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
- 48 Henryk Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kraków, Poland.
- 49 Imperial College London, London, UK.
- 50 Horia Hulubei National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele, Romania.
- 51 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA USA.
- 52 NSC Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology (NSC KIPT), Kharkiv, Ukraine.
- 53 STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, UK.
- 54 Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INR RAN), Moscow, Russia.
- 55 Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, AGH-University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland.
- 56 Sezione INFN di Milano, Milan, Italy.
- 57 Institut für Physik, Universität Rostock, Rostock, Germany.
- 58 Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics, VU University Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 59 National Research Centre Kurchatov Institute, Moscow, Russia.
- 60 Instituto de Fisica Corpuscular (IFIC), Universitat de Valencia-CSIC, Valencia, Spain.
- 61 School of Physics, University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland.
- 62 Institute for Nuclear Research of the National Academy of Sciences (KINR), Kyiv, Ukraine.
- 63 KVI, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 64 Sezione INFN di Bari, Bari, Italy.
- 65 Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey.
- 66 Institute of Particle Physics, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, Hubei China.
- PMID: 26190939
- PMCID: PMC4498677
- DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-015-3502-x
Abstract
The production of the [Formula: see text] state in proton-proton collisions is probed via its decay to the [Formula: see text] final state with the LHCb detector, in the rapidity range [Formula: see text] and in the meson transverse-momentum range [Formula: see text]. The cross-section for prompt production of [Formula: see text] mesons relative to the prompt [Formula: see text] cross-section is measured, for the first time, to be [Formula: see text] at a centre-of-mass energy [Formula: see text] using data corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 0.7 fb[Formula: see text], and [Formula: see text] at [Formula: see text] using 2.0 fb[Formula: see text]. The uncertainties quoted are, in order, statistical, systematic, and that on the ratio of branching fractions of the [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] decays to the [Formula: see text] final state. In addition, the inclusive branching fraction of [Formula: see text]-hadron decays into [Formula: see text] mesons is measured, for the first time, to be [Formula: see text], where the third uncertainty includes also the uncertainty on the [Formula: see text] inclusive branching fraction from [Formula: see text]-hadron decays. The difference between the [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] meson masses is determined to be [Formula: see text].
Figures
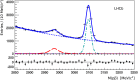
Fig. 1
Proton–antiproton invariant mass spectrum for…
Fig. 1
Proton–antiproton invariant mass spectrum for candidates originating from a secondary vertex and reconstructed…

Fig. 2
Proton–antiproton invariant mass spectrum for…
Fig. 2
Proton–antiproton invariant mass spectrum for candidates originating from a primary vertex ( upper…

Fig. 3
Transverse momentum spectra for
Fig. 3
Transverse momentum spectra for mesons ( red…
References
-
- LHCb collaboration, R. Aaij et al., Measurement of production in collisions at TeV. Eur. Phys. J. C 71, 1645 (2011). arXiv:1103.0423
-
- LHCb collaboration, R. Aaij et al., Measurement of polarization in collisions at TeV. Eur. Phys. J. C 73, 2631 (2013). arXiv:1307.6379 - PMC - PubMed
-
- LHCb collaboration, R. Aaij et al., Production of and mesons in collisions at TeV. JHEP 06, 064 (2013). arXiv:1304.6977
-
- CMS collaboration, S. Chatrchyan et al., and production in collisions at . JHEP 02, 011 (2012). arXiv:1111.1557
-
- ATLAS collaboration, G. Aad et al., Measurement of the differential cross-sections of inclusive, prompt and non-prompt production in proton–proton collisions at . Nucl. Phys. B 850, 387 (2011). arXiv:1104.3038
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
