Novel Chalcone-Thiazole Hybrids as Potent Inhibitors of Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 26191371
- PMCID: PMC4499817
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00169
Novel Chalcone-Thiazole Hybrids as Potent Inhibitors of Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
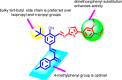
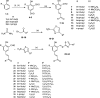
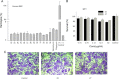
A series of novel hybrids possessing chalcone and thiazole moieties were synthesized and evaluated for their antibacterial activities. In general this class of hybrids exhibited potency against Staphylococcus aureus, and in particular, compound 27 exhibited potent inhibitory activity with respect to other synthesized hybrids. Furthermore, the hemolytic and toxicity data demonstrated that the compound 27 was nonhemolytic and nontoxic to mammalian cells. The in vivo studies utilizing a S. aureus septicemia model demonstrated that compound 27 was as potent as vancomycin. The results of antibacterial activities underscore the potential of this scaffold that can be utilized for developing a new class of novel antibiotics.
Keywords: Chalcone−thiazole hybrids; MIC; Staphylococcus aureus; antibacterial activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. In Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); CDC: Atlanta, GA, 2013; available from http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/pdf/ar-threats-2013....
-
- Chugh T. D. Emerging and re-emerging bacterial diseases in India. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 549–555. - PubMed
-
- Donadio S.; Maffioli S.; Monciardini P.; Sosio M.; Jabes D. Antibiotic discovery in the twenty-first century: current trends and future perspectives. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 423–430. - PubMed
-
- Livermore D. M. The need for new antibiotics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10 (Suppl 4), 1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

