Increased Levels of NF-kB-Dependent Markers in Cancer-Associated Deep Venous Thrombosis
- PMID: 26192925
- PMCID: PMC4507873
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132496
Increased Levels of NF-kB-Dependent Markers in Cancer-Associated Deep Venous Thrombosis
Abstract
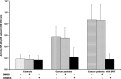
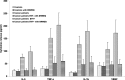
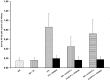
Several studies highlight the role of inflammatory markers in thrombosis as well as in cancer. However, their combined role in cancer-associated deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and the molecular mechanisms, involved in its pathophysiology, needs further investigations. In the present study, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1β), matrix metalloproteases-9 (MMP-9), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tissue factor (TF), fibrinogen and soluble P-selectin, were analyzed in plasma and in monocyte samples from 385 cancer patients, of whom 64 were concomitantly affected by DVT (+). All these markers were higher in cancer patients DVT+ than in those DVT-. Accordingly, significantly higher NF-kB activity was observed in cancer patients DVT+ than DVT-. Significant correlation between data obtained in plasma and monocyte samples was observed. NF-kB inhibition was associated with decreased levels of all molecules in both cancer DVT+ and DVT-. To further demonstrate the involvement of NF-kB activation by the above mentioned molecules, we treated monocyte derived from healthy donors with a pool of sera from cancer patients with and without DVT. These set of experiments further suggest the significant role played by some molecules, regulated by NF-kB, and detected in cancer patients with DVT. Our data support the notion that NF-kB may be considered as a therapeutic target for cancer patients, especially those complicated by DVT. Treatment with NF-kB inhibitors may represent a possible strategy to prevent or reduce the risk of DVT in cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Sallah S, Wan JY, Nguyen NP. Venous thrombosis in patients with solid tumors: determination of frequency and characteristics. Thromb Haemost. 2002; 7: 575–579. - PubMed
-
- Wun T, White RH. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Cancer Invest. 2009; 27: S63–S74. - PubMed
-
- Haddad TC, Greeno EW. Chemotherapy-induced thrombosis. Thromb Res 2006; 118: 555–568. - PubMed
-
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5: 632–634. - PubMed
-
- Rickles FR, Falanga A. Molecular basis for the relationship between thrombosis and cancer. Thromb Res. 2001; 102: V215–224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

