Recognition of xyloglucan by the crystalline cellulose-binding site of a family 3a carbohydrate-binding module
- PMID: 26193423
- PMCID: PMC5877785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.07.009
Recognition of xyloglucan by the crystalline cellulose-binding site of a family 3a carbohydrate-binding module
Abstract
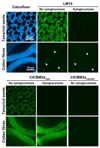
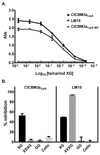
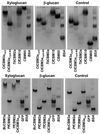
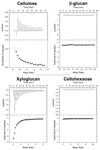
Type A non-catalytic carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs), exemplified by CtCBM3acipA, are widely believed to specifically target crystalline cellulose through entropic forces. Here we have tested the hypothesis that type A CBMs can also bind to xyloglucan (XG), a soluble β-1,4-glucan containing α-1,6-xylose side chains. CtCBM3acipA bound to xyloglucan in cell walls and arrayed on solid surfaces. Xyloglucan and cellulose were shown to bind to the same planar surface on CBM3acipA. A range of type A CBMs from different families were shown to bind to xyloglucan in solution with ligand binding driven by enthalpic changes. The nature of CBM-polysaccharide interactions is discussed.
Keywords: CBM3a; Carbohydrate-binding module; Crystalline cellulose; Plant cell wall; Xyloglucan.
Copyright © 2015 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Gilbert HJ, Knox JP, Boraston AB. Advances in understanding the molecular basis of plant cell wall polysaccharide recognition by carbohydrate-binding modules. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013;23:669–677. - PubMed
-
- Raghothama S, Simpson PJ, Szabo L, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, Williamson MP. Solution structure of the CBM10 cellulose binding module from Pseudomonas xylanase A. Biochemistry. 2000;39:978–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

