β-Catenin destruction complex-independent regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by APC in intestinal tumorigenesis
- PMID: 26193883
- PMCID: PMC4526734
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.264515.115
β-Catenin destruction complex-independent regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by APC in intestinal tumorigenesis
Abstract
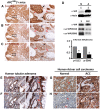
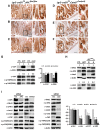
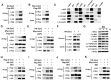
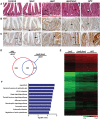
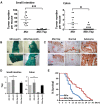
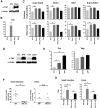
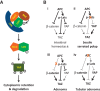
Mutations in Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) underlie familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an inherited cancer syndrome characterized by the widespread development of colorectal polyps. APC is best known as a scaffold protein in the β-catenin destruction complex, whose activity is antagonized by canonical Wnt signaling. Whether other effector pathways mediate APC's tumor suppressor function is less clear. Here we report that activation of YAP, the downstream effector of the Hippo signaling pathway, is a general hallmark of tubular adenomas from FAP patients. We show that APC functions as a scaffold protein that facilitates the Hippo kinase cascade by interacting with Sav1 and Lats1. Consistent with the molecular link between APC and the Hippo signaling pathway, genetic analysis reveals that YAP is absolutely required for the development of APC-deficient adenomas. These findings establish Hippo-YAP signaling as a critical effector pathway downstream from APC, independent from its involvement in the β-catenin destruction complex.
Keywords: APC; Hippo signaling; TAZ; YAP; tumorigenesis; β-catenin.
© 2015 Cai et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham SC, Wu T-T, Hruban RH, Lee J-H, Yeo CJ, Conlon K, Brennan M, Cameron JL, Klimstra DS. 2002. Genetic and immunohistochemical analysis of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: frequent allelic loss on chromosome 11p and alterations in the APC/β-catenin pathway. Am J Pathol 160: 953–962. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoki K, Taketo MM. 2007. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC): a multi-functional tumor suppressor gene. J Cell Sci 120: 3327–3335. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Zanconato F, Bresolin S, Forcato M, Basso G, Bicciato S, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. 2012. Role of TAZ as mediator of Wnt signaling. Cell 151: 1443–1456. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V. 2014. YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 158: 157–170. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ. 2007. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449: 1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
