The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 2 PET Core: 2015
- PMID: 26194311
- PMCID: PMC4510459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.05.001
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 2 PET Core: 2015
Abstract
Introduction: This article reviews the work done in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative positron emission tomography (ADNI PET) core over the past 5 years, largely concerning techniques, methods, and results related to amyloid imaging in ADNI.
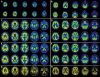
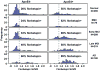
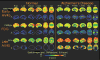
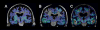
Methods: The PET Core has used [(18)F]florbetapir routinely on ADNI participants, with over 1600 scans available for download. Four different laboratories are involved in data analysis, and have examined factors such as longitudinal florbetapir analysis, use of [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET in clinical trials, and relationships between different biomarkers and cognition.
Results: Converging evidence from the PET Core has indicated that cross-sectional and longitudinal florbetapir analyses require different reference regions. Studies have also examined the relationship between florbetapir data obtained immediately after injection, which reflects perfusion, and FDG-PET results. Finally, standardization has included the translation of florbetapir PET data to a centiloid scale.
Conclusion: The PET Core has demonstrated a variety of methods for the standardization of biomarkers such as florbetapir PET in a multicenter setting.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid; Fluorodeoxyglucose; Mild cognitive impairment; PET imaging.
Copyright © 2015 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain. New York: Thieme; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

